13 Leadership, Roles, and Problem Solving in Groups
Introduction
13.1 Group Member Roles
Task-Related Roles and Behaviors
Task roles and their related behaviors contribute directly to the group’s completion of a task or achievement of its goal or purpose. Task-related roles typically serve leadership, informational, or procedural functions. In this section, we will discuss the following roles and behaviors: task leader, expediter, information provider, information seeker, gatekeeper, and recorder.
Task Leader
Within any group, there may be a task leader. This person may have a high group status because of his or her maturity, problem-solving abilities, knowledge, and/or leadership experience and skills. This person acts to help the group complete its task (Cragan & Wright, 1991). This person may be a designated or emergent leader, but in either case, task leaders tend to talk more during group interactions than other group members and also tend to do more work in the group. Depending on the number of tasks a group has, there may be more than one task leader, especially if the tasks require different sets of skills or knowledge. Because of the added responsibilities of being a task leader, people in these roles may experience higher levels of stress. A task leader could lessen these stresses, however, through some of the maintenance role behaviors that will be discussed later.
We can divide task-leader behaviors two types: substantive and procedural (Pavitt, 1999). The substantive leader is the “idea person” who communicates “big picture” thoughts and suggestions that feed group discussion. The procedural leader is the person who gives the most guidance, perhaps following up on the ideas generated by the substantive leader. A skilled and experienced task leader may be able to perform both of these roles, but when the roles are filled by two different people, the person considered the procedural leader is more likely than the substantive leader to be viewed by members as the overall group leader. This indicates that task-focused groups assign more status to the person who actually guides the group toward the completion of the task (a “doer”) than the person who comes up with ideas (the “thinker”).
Expediter
The expediter is a task-related role that functions to keep the group on track toward completing its task by managing the agenda and setting and assessing goals in order to monitor the group’s progress (Burke, Georganta, & Marlow, 2019). An expediter doesn’t push group members mindlessly along toward the completion of their task; an expediter must have a good sense of when a topic has been sufficiently discussed or when a group’s extended focus on one area has led to diminishing returns. In such cases, the expediter may say, “Now that we’ve had a thorough discussion of the pros and cons of switching the office from PCs to Macs, which side do you think has more support?” or “We’ve spent half of this meeting looking for examples of what other libraries have done and haven’t found anything useful. Maybe we should switch gears so we can get something concrete done tonight.”
To avoid the perception that group members are being rushed, a skilled expediter can demonstrate good active-listening skills by paraphrasing what has been discussed and summarizing what has been accomplished in such a way that makes it easier for group members to see the need to move on.
Information Provider
The information provider role includes behaviors that are more evenly shared compared to other roles, as ideally, all group members present new ideas, initiate discussions of new topics, and contribute their own relevant knowledge and experiences Burke, Georganta, & Marlow, 2019). When group members meet, they each possess different types of information. Early group meetings may consist of group members taking turns briefing each other on their area of expertise. In other situations, one group member may be chosen because of his or her specialized knowledge. This person may be the primary information provider for all other group members. For example, one of our colleagues was selected to serve on a university committee reviewing our undergraduate learning goals. Since her official role was to serve as the “faculty expert” on the subcommittee related to speaking, she played a more central information-provider function for the group during most of the initial meetings. Since other people on the subcommittee were not as familiar with speaking and its place within higher education curriculum, it made sense that information-providing behaviors were not as evenly distributed.
Information Seeker
The information seeker asks for more information, elaboration, or clarification on items relevant to the group’s task Burke, Georganta, & Marlow, 2019). The information sought may include facts or group member opinions. In general, information seekers ask questions for clarification, but they can also ask questions that help provide an important evaluative function. Most groups could benefit from more critically oriented information-seeking behaviors. As our discussion of groupthink notes, critical questioning helps increase the quality of ideas and group outcomes and helps avoid groupthink. By asking for more information, people have to defend (in a non-adversarial way) and/or support their claims, which can help ensure that the information is credible, relevant, and thoroughly considered. When information seeking or questioning occurs because of poor listening skills, it risks negatively affecting the group. Skilled information providers and seekers are also good active listeners. They increase all group members’ knowledge when they paraphrase and ask clarifying questions about the information presented.
Gatekeeper
The gatekeeper manages the flow of conversation in a group in order to achieve an appropriate balance so that all group members get to participate in a meaningful way Burke, Georganta, & Marlow, 2019). The gatekeeper may prompt others to provide information by saying something like “Let’s each share one idea we have for a movie to show during Black History Month.” He or she may also help correct an imbalance between members who have provided much information already and members who have been quiet by saying something like “Aretha, we’ve heard a lot from you today. Let us hear from someone else. Beau, what are your thoughts on Aretha’s suggestion?” Gatekeepers should be cautious about “calling people out” or at least making them feel that way. Instead of scolding someone for not participating, the gatekeeper should be ask a member to contribute something specific instead of just asking if that person has anything to add. Since gatekeepers make group members feel included, they also service the relational aspects of the group.
Recorder
The recorder takes notes on the discussion and activities that occur during a group meeting. The recorder is the only role that is essentially limited to one person at a time since in most cases it would not be necessary or beneficial to have more than one person recording. At less formal meetings, there may be no recorder, while at formal meetings there is usually a person who records meeting minutes, which are an overview of what occurred at the meeting. Each committee will have different rules or norms regarding the level of detail within and availability of the minutes.
Maintenance Roles and Behaviors
Maintenance roles and their corresponding behaviors function to create and maintain social cohesion and fulfill the interpersonal needs of group members. All these role behaviors require strong and sensitive interpersonal skills. The maintenance roles we will discuss in this section include social-emotional leader, supporter, tension releaser, harmonizer, and interpreter.
Social-Emotional Leader

The social-emotional leader within a group may perform a variety of maintenance roles and is generally someone who is well liked by the other group members and whose role behaviors complement but do not compete with the task leader. The social-emotional leader may also reassure and support the task leader when he or she is stressed (Koch, 2013). In general, the social-emotional leader is a reflective thinker who has good perception skills that he or she uses to analyze the group dynamics and climate and then initiate the appropriate role behaviors to maintain a positive climate. This is not a role that shifts from person to person. While all members of the group perform some maintenance role behaviors at various times, the socioemotional leader reliably functions to support group members and maintain a positive relational climate. Social-emotional leadership functions can actually become detrimental to the group and lead to less satisfaction among members when they view maintenance behaviors as redundant or as too distracting from the task (Pavitt, 1999).
Supporter
The role of supporter is characterized by communication behaviors that encourage other group members and provide emotional support as needed (Koch, 2013). The supporter’s work primarily occurs in one-on-one exchanges that are more intimate and in-depth than the exchanges that take place during full group meetings. While many group members may make supporting comments publicly at group meetings, these comments are typically superficial and/or brief. A supporter uses active empathetic listening skills to connect with group members who may seem down or frustrated by saying something like “Tayesha, you seemed kind of down today. Is there anything you’d like to talk about?” Supporters also follow up on previous conversations with group members to maintain the connections they have already established by saying things like “Alan, I remember you said your mom is having surgery this weekend. I hope it goes well. Let me know if you need anything.”
Tension Releaser
The tension releaser is someone who is naturally funny and sensitive to the personalities of the group and the dynamics of any given situation and who uses these qualities to manage the frustration level of the group (Koch, 2013). Being funny is not enough to fulfill this role, as jokes or comments could indeed be humorous to other group members but are delivered at an inopportune time, which ultimately creates rather than releases tension. The healthy use of humor by the tension releaser performs the same maintenance function as the empathy employed by the harmonizer or the social-emotional leader, but it is less intimate and is typically directed toward the whole group instead of just one person.
Harmonizer
Group members who help manage the various types of group conflict that emerge during group communication plays the harmonizer role (Koch, 2013). They keep their eyes and ears open for signs of conflict among group members and ideally intervene before it escalates. For example, the harmonizer may sense that one group member’s critique of another member’s idea was not received positively, and he or she may be able to rephrase the critique in a more constructive way, which can help diminish the other group member’s defensiveness. Harmonizers also deescalate conflict once it has already started—for example, by suggesting that the group take a break and then mediating between group members in a side conversation.
These actions can help prevent conflict from spilling over into other group interactions. In cases where the whole group experiences conflict, the harmonizer may help lead the group in perception-checking discussions that help members see an issue from multiple perspectives. For a harmonizer to be effective, he or she must be viewed as impartial and committed to the group as a whole rather than to one side, person, or faction within the larger group. A special kind of harmonizer that helps manage cultural differences within the group is the interpreter.
Interpreter
An interpreter helps manage the diversity within a group by mediating intercultural conflict, articulating common ground between different people, and generally creating a climate where difference is seen as an opportunity rather than as something to be feared (Koch, 2013). Just as an interpreter at the United Nations acts as a bridge between two different languages, the interpreter can bridge identity differences between group members. Interpreters can help perform the other maintenance roles discussed with a special awareness of and sensitivity toward cultural differences. Interpreters, because of their cultural sensitivity, may also take a proactive role to help address conflict before it emerges—for example, by taking a group member aside and explaining why his or her behavior or comments may be perceived as offensive.
Negative Roles and Behaviors
Group communication scholars began exploring the negative side of group member roles more than sixty years ago (Benne & Sheats, 1948). Studying these negative roles can help us analyze group interactions and potentially better understand why some groups are more successful than others are. It is important to acknowledge that we all perform some negative behaviors within groups but that those behaviors do not necessarily constitute a role. A person may temporarily monopolize a discussion to bring attention to his or her idea. If that behavior gets the attention of the group members and makes them realize they were misinformed or headed in a negative direction, then that behavior may have been warranted. Group members may enact negative behaviors with varying degrees of intensity and regularity, and their effects may range from mild annoyance to group failure. In general, the effects grow increasingly negative as they increase in intensity and frequency.
Self-Centered Roles Central Negative
The central negative argues against most of the ideas and proposals discussed in the group and often emerges because of a leadership challenge during group formation. The failed attempt to lead the group can lead to feelings of resentment toward the leader and/or the purpose of the group, which then manifest in negative behaviors that delay, divert, or block the group’s progress toward achieving its goal. This scenario is unfortunate because the central negative is typically a motivated and intelligent group member who can benefit the group if properly handled by the group leader or other members. Group communication scholars suggest that the group leader or leaders actively incorporate central negatives into group tasks and responsibilities to make them feel valued and to help diminish any residual anger, disappointment, or hurt feelings from the leadership conflict (Bormann & Bormann, 1988). Otherwise, the central negative will continue to argue against the proposals and decisions of the group, even when they may agree. In some cases, the central negative may unintentionally serve a beneficial function if his or her criticisms prevent groupthink.
Monopolizer
The monopolizer is a group member who makes excessive verbal contributions, preventing equal participation by other group members. In short, monopolizers like to hear the sound of their own voice and do not follow typical norms for conversational turn taking. Some people who are well-informed, charismatic, and competent communicators can get away with impromptu lectures and long stories, but monopolizers do not possess the magnetic qualities of such people. A group member’s excessive verbal contributions are more likely to be labeled as monopolizing when they are not related to the task or when they provide unnecessary or redundant elaboration. Some monopolizers do not intentionally speak for longer than they should. Instead, they think they are making a genuine contribution to the group. These folks likely lack sensitivity to nonverbal cues, or they would see that other group members are tired of listening or annoyed. Other monopolizers just like to talk and do not care what others think. Some may be trying to make up for a lack of knowledge or experience. This type of monopolizer is best described as a dilettante, or an amateur who tries to pass himself or herself off as an expert.
Several subgroups of behaviors fall under the monopolizer’s role. The “stage hog” monopolizes discussion with excessive verbal contributions and engages in one-upping and narcissistic listening. Gaining an advantage over is a spotlight-stealing strategy in which people try to verbally “out-do” others by saying something like “You think that’s bad? Listen to what happened to me!” They also listen to others in order to find something they can connect back to themselves, not to understand the message. The stage hog is like the diva that refuses to leave the stage to let the next performer begin. Unlike a monopolizer, who may engage in his or her behaviors unknowingly, stage hogs are usually aware of what they are doing.
The “egghead” monopolizes the discussion with excessive contributions based in actual knowledge. However, those contributions exceed the level of understanding of other group members or the needs of the group (Cragan & Wright, 1999). The egghead is different from the dilettante monopolizer discussed earlier because this person has genuine knowledge and expertise on a subject, which may be useful to the group. Nevertheless, like the monopolizer and stage hog, the egghead’s excessive contributions draw attention away from the task, slow the group down, and may contribute to a negative group climate. The egghead may be like an absentminded professor who is smart but lacks the social sensitivity to tell when he or she has said enough and is now starting to annoy other group members. This type of egghead naively believes that other group members care as much about the subject as he or she does.
The second type of egghead is more pompous and monopolizes the discussion to flaunt his or her intellectual superiority. While the group may tolerate the first type of egghead to a point, the group may perceive the second type of egghead more negatively and as one who will hurt the group. In general, the egghead’s advanced subject knowledge and excessive contributions can hurt the group’s potential for synergy, since other group members may defer to the egghead expert, which can diminish the creativity that comes from outside and non-expert perspectives.
13.2 Problem Solving and Decision Making in Groups
Group Problem Solving
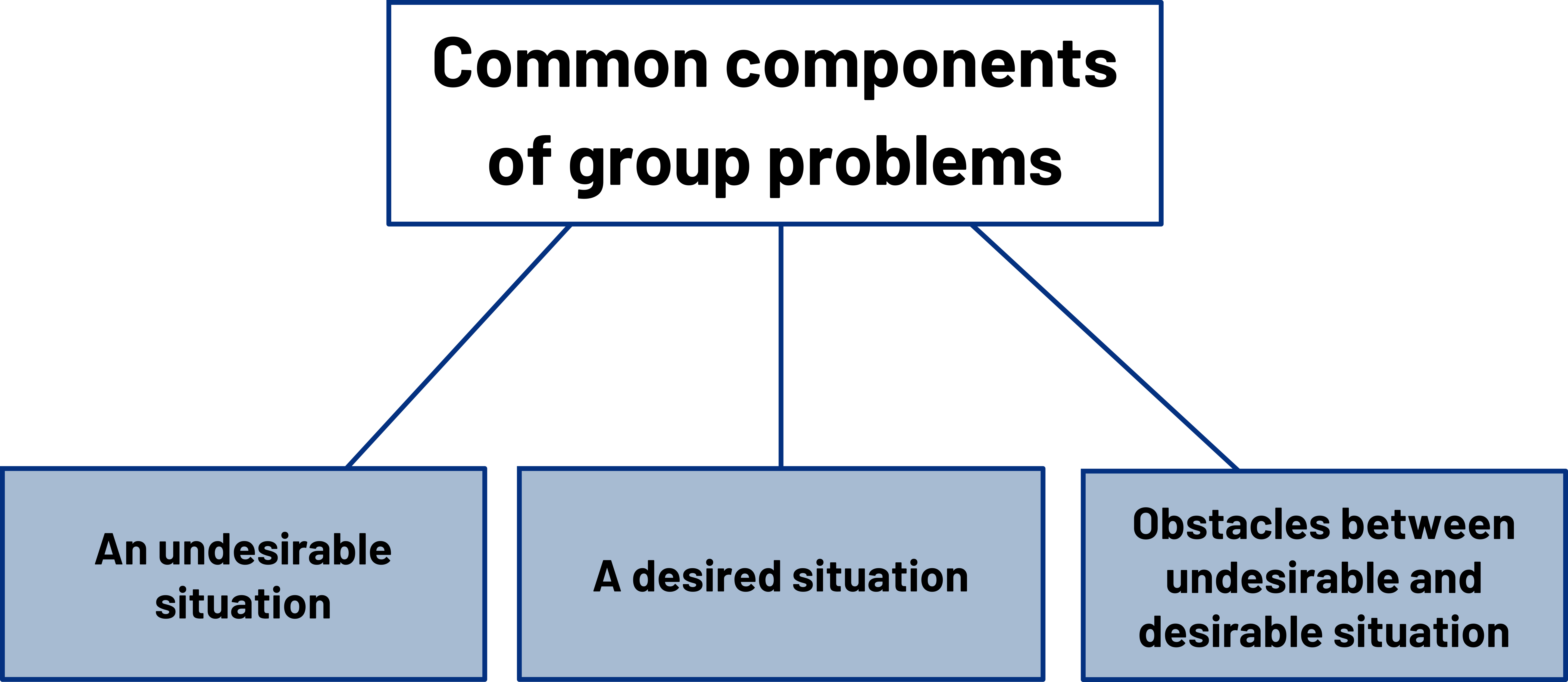
The problem-solving process involves thoughts, discussions, actions, and decisions that occur from the first consideration of a problematic situation to the goal. The problems that groups face are varied, but some common problems include budgeting funds, raising funds, planning events, addressing customer or citizen complaints, creating or adapting products or services to fit needs, supporting members, and raising awareness about issues or causes. Problems of all sorts have three common components (Adams & Galanes, 2009):
- An undesirable situation. When conditions are desirable, there is not a problem.
- A desired situation. Even though it may only be a vague idea, there is a drive to better the undesirable situation. The vague idea may develop into a more precise goal that can be achieved, although solutions are not yet generated.
- Obstacles between undesirable and desirable situation. These things stand in the way between the current situation and the group’s goal of addressing it. This component of a problem requires the most work, and it is the part where decision-making occurs. Some examples of obstacles include limited funding, resources, personnel, time, or information. Obstacles can also take the form of people who are working against the group, including people resistant to change or people who disagree.
Discussion of these three elements of a problem helps the group tailor its problem-solving process, as each problem will vary. While these three general elements are present in each problem, the group should also address specific characteristics of the problem. Five common and important characteristics to consider are task difficulty, number of possible solutions, group member interest in problem, group member familiarity with problem, and the need for solution acceptance (Adams & Galanes, 2009).
- Task difficulty. Difficult tasks are also typically more complex. Groups should be prepared to spend time researching and discussing a difficult and complex task in order to develop a shared foundational knowledge. This typically requires individual work outside of the group and frequent group meetings to share information.
- Number of possible solutions. There are usually multiple ways to solve a problem or complete a task, but some problems have more potential solutions than others do. Figuring out how to prepare a beach house for an approaching hurricane is fairly complex and difficult, but there are still a limited number of things to do—for example, taping and boarding up windows; turning off water, electricity, and gas; trimming trees; and securing loose outside objects. Other problems may require more creativity. For example, designing a new restaurant may entail using some standard solutions but could also entail many different types of innovation with layout and design.
- Group member interest in problem. When group members are interested in the problem, they will be more engaged with the problem-solving process and invested in finding a quality solution. Groups with high interest in and knowledge about the problem may want more freedom to develop and implement solutions, while groups with low interest may prefer a leader who provides structure and direction.
- Group familiarity with problem. Some groups encounter a problem regularly, while other problems are unique or unexpected. A family who has lived in hurricane alley for decades probably has a better idea of how to prepare its house for a hurricane than does a family that just recently moved from the Midwest. Many groups that rely on funding have to revisit a budget every year, and in recent years, groups have had to get more creative with budgets due to funding cuts in nearly every sector. When group members are not familiar with a problem, they will need to do background research on what similar groups have done. They may want to bring in outside experts.
- Need for solution acceptance. In this step, groups must consider how many people the decision will affect and how much “buy-in” from others the group needs in order implement their solution successfully. Some small groups have many stakeholders on whom the success of a solution depends. Other groups are answerable only to themselves. In such cases, groups will want to poll those who will be affected by the solution. They may want to do a pilot implementation to see how people react. Imposing an excellent solution that does not have buy-in from stakeholders can still lead to failure.
Group Problem-Solving Process
There are several variations of similar problem-solving models based on scholar John Dewey’s reflective thinking process (Bormann & Bormann, 1988). As you read the steps in the process, think about how you can apply what we learned regarding the general and specific elements of problems.

Step 1: Define the Problem
Define the problem by considering the three elements shared by every problem: the current undesirable situation, the goal or more desirable situation, and obstacles in the way (Adams & Galanes, 2009). At this stage, group members share what they know about the current situation, without proposing solutions or evaluating the information. Here are some questions to ask during this stage: What is the current difficulty? How did we come to know that the difficulty exists? Who or what is involved? Why is it meaningful/urgent/important? What have the effects been so far? What, if any, elements of the difficulty require clarification?
At the end of this stage, the group should be able to compose a single sentence that summarizes the problem called a problem statement. Avoid wording in the problem statement or question that hints at potential solutions. A small group formed to investigate ethical violations of city officials could use the following problem statement: “Our state does not currently have a mechanism for citizens to report suspected ethical violations by city officials.”
Step 2: Analyze the Problem
During this step, a group should analyze the problem and the group’s relationship to the problem. Whereas the first step involved exploring the “what” related to the problem, this step focuses on the “why.” At this stage, group members can discuss the potential causes of the difficulty. Group members may also want to begin setting out an agenda or timeline for the group’s problem-solving process, looking forward to the other steps. To analyze the problem, the group can discuss the five common problem variables discussed before. Here are two examples of questions that the group formed to address ethics violations might ask: Why doesn’t our city have an ethics reporting mechanism? Do cities of similar size have such a mechanism? Once the problem has been analyzed, the group can pose a problem question that will guide the group as it generates possible solutions. “How can citizens report suspected ethical violations of city officials and how will such reports be processed and addressed?” As you can see, the problem question is more complex than the problem statement, since the group has moved on to more in-depth discussion of the problem during step 2.
Step 3: Generate Possible Solutions
During this step, group members generate possible solutions to the problem. Again, do not evaluate solutions at this point, only propose and clarify. The question should be what could we do to address this problem, not what should we do to address it? It is perfectly OK for a group member to question another person’s idea by asking something like “What do you mean?” or “Could you explain your reasoning more?” Discussions at this stage may reveal a need to return to previous steps to better define or more fully analyze a problem. Since many problems are multifaceted, it is necessary for group members to generate solutions for each part of the problem separately, making sure to have multiple solutions for each part. Stopping the solution-generating process prematurely can lead to groupthink.
Step 4: Evaluate Solutions
During this step, solutions can be critically evaluated based on their credibility, completeness, and worth. Once the potential solutions have been narrowed based on differences in relevance and/or merit, the group should analyze each solution based on its potential effects—especially negative effects. Groups that are required to report the rationale for their decision or whose decisions may be subject to public scrutiny would be wise to make a set list of criteria for evaluating each solution.
Additionally, solutions can be evaluated based on how well they fit with the group’s charge and the abilities of the group. To do this, group members may ask, “Does this solution live up to the original purpose or mission of the group?” “Can the solution actually be implemented with our current resources and connections?” “How will this solution be supported, funded, enforced, and assessed?” Secondary tensions and substantive conflict, two concepts discussed earlier, emerge during this step of problem solving, and group members will need to employ effective critical thinking and listening skills.
Decision-making is part of the larger process of problem solving and it plays a prominent role in this step. While there are several similar models for problem solving, groups can use many varied decision-making techniques. For example, to narrow the list of proposed solutions, group members may decide by majority vote, by weighing the pros and cons, or by discussing them until they reach a consensus. There are also more complex decision-making models like the “six hats method,” which we will discuss later. Once the group reaches a final decision, the group leader or facilitator should confirm that the group agrees. It may be beneficial to let the group break for a while or even to delay the final decision until a later meeting to allow people time to evaluate it outside of the group context.
Step 5: Implement and Assess the Solution
Implementing the solution requires some advanced planning, and it should not be rushed unless the group is operating under strict time restraints or a delay may lead to some kind of harm. Although some solutions can be implemented immediately, others may take days, months, or years. As was noted earlier, it may be beneficial for groups to poll those who will be affected by the solution as to their opinion of it or even to do a pilot test to observe the effectiveness of the solution and how people react to it. Before implementation, groups should also determine how and when they would assess the effectiveness of the solution by asking, “How will we know if the solution is working or not?” Since solution assessment will vary based on whether or not the group is disbanded, groups should also consider the following questions: If the group disbands after implementation, who will be responsible for assessing the solution? If the solution fails, will the same group reconvene? Will a new group be formed?
Certain elements of the solution may need to be delegated to various people inside and outside the group. Group members may also be assigned to implement a particular part of the solution based on their role or because it connects to their area of expertise. Likewise, group members may be tasked with publicizing the solution or “selling” it to a particular group of stakeholders. Last, the group should consider its future. In some cases, the group will get to decide if it will stay together and continue working on other tasks or if it will disband. In other cases, outside forces determine the group’s fate.
Decision Making in Groups
We all engage in personal decision making daily, and we all know that some decisions are more difficult than others are. When we make decisions in groups, we face some challenges that we do not face in our personal decision-making, but we also stand to benefit from some advantages of group decision-making (Napier & Gershenfeld, 2004). Group decision making can appear fair and democratic but really only be a gesture that covers up the fact that certain group members or the group leader have already decided. Group decision making also takes more time than individual decisions and can be burdensome if some group members do not do their assigned work, divert the group with self-centered or unproductive role behaviors, or miss meetings.
Conversely, though, group decisions are often more informed, since all group members develop a shared understanding of a problem through discussion and debate. The shared understanding may also be more complex and deep than what an individual would develop, because group members expose themselves to a variety of viewpoints that can broaden their own perspectives. Group decisions also benefit from synergy, one of the key advantages of group communication that we discussed earlier. Most groups do not use a specific method of decision-making, perhaps thinking that they will work things out as they go. This can lead to unequal participation, social loafing, premature decisions, prolonged discussion, and a host of other negative consequences. Therefore, in this section we will learn some practices that will prepare us for good decision-making and some specific techniques we can use to help us reach a final decision.
Brainstorming Before Decision Making

Before groups can make a decision, they need to generate possible solutions to their problem. The most commonly used method is brainstorming, although most people do not follow the recommended steps of brainstorming. As you will recall, brainstorming refers to the quick generation of ideas free of evaluation. The originator of the term brainstorming said the following four rules must be followed for the technique to be effective (Osborn, 1959):
- Evaluation of ideas is forbidden.
- Wild and crazy ideas are encouraged.
- Quantity of ideas, not quality, is the goal.
- New combinations of ideas presented are encouraged.
To make brainstorming more of a decision-making method rather than an idea-generating method, group communication scholars have suggested additional steps that precede and follow brainstorming (Cragan & Wright, 1991).
- Do a warm-up brainstorming session. Some people are more apprehensive about publicly communicating their ideas than others are, and a warm-up session can help ease apprehension and prime group members for task-related idea generation. Anyone in the group can initiate the short warm-up. To get things started, a person could ask, “If our group formed a band, what would we be called?” or “What other purposes could a mailbox serve?” In the previous examples, the first warm up gets the group’s creative juices flowing, while the second focuses more on practical and concrete ideas.
- Do the actual brainstorming session. This session should not last more than thirty minutes and should follow the four rules of brainstorming mentioned previously. In order to realize the fourth rule, the facilitator could encourage people to piggyback off each other’s ideas.
- Eliminate duplicate ideas. After the brainstorming session is over, group members can eliminate (without evaluating) ideas that are the same or very similar.
- Clarify, organize, and evaluate ideas. Before evaluation, see if any ideas need clarification. Then try to theme or group ideas together in some orderly fashion. Since “wild and crazy” ideas are encouraged, some suggestions may need clarification. If it becomes clear that there is not really a foundation to an idea and that it is too vague or abstract, it may be eliminated. As a caution, though, it may be wise not to throw out off-the-wall ideas that are hard to categorize and instead put them in a miscellaneous or “wild and crazy” category.
Discussion Before Decision Making
The nominal group technique guides decision making through a four-step process that includes idea generation and evaluation and seeks to elicit equal contributions from all group members (Delbecq & Van de Ven, 1971). This method is useful because the procedure involves all group members systematically, which fixes the problem of uneven participation during discussions. Since everyone contributes to the discussion, this method can also help reduce instances of social loafing. To use the nominal group technique, do the following:
- Silently and individually, list ideas.
- Create a master list of ideas.
- Clarify ideas as needed.
- Take a secret vote to rank group members’ acceptance of ideas.
During the first step, have group members work quietly, in the same space, to write down every idea they have to address the task or problem they face. This should not take more than twenty minutes. Whoever is facilitating the discussion should remind group members to use brainstorming techniques, which means they should not evaluate ideas as they are generated. Ask group members to remain silent once they have finished their list so they do not distract others.
During the second step, the facilitator goes around the group in a consistent order asking each person to share one idea at a time. As the idea is shared, the facilitator records it on a master list that everyone can see. Keep track of how many times each idea comes up, as that could be an idea that warrants more discussion. Continue this process until all the ideas have been shared. As a note to facilitators, some group members may begin to edit their list or self-censor when asked to provide one of their ideas. To limit a person’s apprehension with sharing his or her ideas and to ensure that each idea is shared, I have asked group members to exchange lists with someone else so they can share ideas from the list they receive without fear of being judged.
During step three, the facilitator should note that group members could now ask for clarification on ideas on the master list. Do not let this discussion stray into evaluation of ideas. To help avoid an unnecessarily long discussion, it may be useful to go from one person to the next to ask which ideas need clarifying and then go to the originator(s) of the idea in question for clarification.
During the fourth step, members use a voting ballot to rank the acceptability of the ideas on the master list. If the list is long, you may ask group members to rank only their top five or so choices. The facilitator then takes up the secret ballots and reviews them in a random order, noting the rankings of each idea. Ideally, the highest ranked idea can then be discussed and decided on. The nominal group technique does not carry a group all the way through to the point of decision; rather, it sets the group up for a roundtable discussion or use of some other method to evaluate the merits of the top ideas.
Specific Decision-Making Techniques
Some decision-making techniques involve determining a course of action based on the level of agreement among the group members. These methods include majority, expert, authority, and consensus rule. Table 14.1 “Pros and Cons of Agreement-Based Decision-Making Techniques” reviews the pros and cons of each of these methods.
Majority rule is a commonly used decision-making technique in which a majority (one-half plus one) must agree before making a decision (Schippers & Rus, 2021). A show-of-hands vote, a paper ballot, or an electronic voting system can determine the majority choice. Many decision-making bodies, including the US House of Representatives, Senate, and Supreme Court, use majority rule to make decisions, which shows that it is often associated with democratic decision making, since each person gets one vote and each vote counts equally. Of course, other individuals and mediated messages can influence a person’s vote, but since the voting power is spread among all group members, it is not easy for one person or party to take control of the decision-making process. In some cases—for example, to override a presidential veto or to amend the constitution—a super majority of two-thirds may be required to make a decision.
Minority rule is a decision-making technique in which a designated authority or expert has final say over a decision and may or may not consider the input of other group members. When a designated expert makes a decision by minority rule, there may be buy-in from others in the group, especially if the members of the group did not have relevant knowledge or expertise. When a designated authority makes decisions, buy-in will vary based on group members’ level of respect for the authority. For example, decisions made by an elected authority may be more accepted by those who elected him or her than by those who did not. As with majority rule, this technique can be time saving. Unlike majority rule, one person or party can have control over the decision-making process.
This type of decision-making is more similar to that used by monarchs and dictators. An obvious negative consequence of this method is that the needs or wants of one person can override the needs and wants of the majority. A minority deciding for the majority has led to negative consequences throughout history. The white Afrikaner minority that ruled South Africa for decades instituted apartheid, which was a system of racial segregation that disenfranchised and oppressed the majority population. The quality of the decision and its fairness really depends on the designated expert or authority.
Consensus rule is a decision-making technique in which all members of the group must agree on the same decision. On rare occasions, a decision may be ideal for all group members, which can lead to unanimous agreement without further debate and discussion. Although this can be positive, be cautious that this is not a sign of groupthink. More typically, groups reach consensus only after lengthy discussion. On the plus side, consensus often leads to high-quality decisions due to the time and effort it takes to get everyone in agreement. Group members are also more likely to be committed to the decision because of their investment in reaching it. On the negative side, the ultimate decision is often one that all group members can live with but not one that is ideal for all members. Additionally, the process of arriving at consensus also includes conflict, as people debate ideas and negotiate the interpersonal tensions that may result.
[table id=10 /]
Influences on Decision Making
Many factors influence the decision-making process. For example, how might a group’s independence or access to resources affect the decisions they make? What potential advantages and disadvantages come with decisions made by groups that are more or less similar in terms of personality and cultural identities? In this section, we will explore how situational, personality, and cultural influences affect decision making in groups.
Situational Influences on Decision-Making
A group’s situational context affects decision-making (Franken & Muris, 2005). One key situational element is the degree of freedom that the group has to make its own decisions, secure its own resources, and initiate its own actions. Some groups have to go through multiple approval processes before they can do anything, while others are self-directed, self-governing, and self-sustaining. Another situational influence is uncertainty. In general, groups deal with more uncertainty in decision-making than do individuals because of the increased number of variables that comes with adding more people to a situation. Individual group members cannot know what other group members are thinking, whether they are doing their work, and how committed they are to the group. Therefore, the size of a group is a powerful situational influence, as it adds to uncertainty and complicates communication.
Access to information also influences a group. First, the nature of the group’s task or problem affects its ability to get information. Group members can more easily make decisions about a problem when other groups have similarly experienced it. Even if the problem is complex and serious, the group can learn from other situations and apply what it learns. Second, the group must have access to flows of information. Access to archives, electronic databases, and individuals with relevant experience is necessary to obtain any relevant information about similar problems or to do research on a new or unique problem. In this regard, group members’ formal and information network connections also become important situational influences.
The origin and urgency of a problem are also situational factors that influence decision-making. In terms of origin, problems usually occur in one of four ways:
- Something goes wrong. Group members must decide how to fix or stop something. Example—a firehouse crew finds out that half of the building is contaminated with mold and must be closed down.
- Expectations change or increase. Group members must innovate more efficient or effective ways of doing something. Example—a firehouse crew finds out that the district they are responsible for is being expanded.
- Something goes wrong and expectations change or increase. Group members must fix/stop and become more efficient/effective. Example—the firehouse crew has to close half the building and must start responding to more calls due to the expanding district.
- The problem existed from the beginning. Group members must go back to the origins of the situation, walk through and analyze the steps again to decide what can be done differently. Example—a firehouse crew has consistently had to work with minimal resources in terms of building space and firefighting tools.
In each of the cases, the need for a decision may be more or less urgent depending on how badly something is going wrong, how high the expectations have been raised, or the degree to which people are fed up with a broken system. Decisions must be made in situations ranging from crisis level to mundane.
Cultural Context and Decision-Making

Just like neighborhoods, schools, and countries, small groups vary in terms of their degree of similarity and difference. Demographic changes in the United States and increases in technology that can bring different people together make it more likely that we will be interacting in more and more heterogeneous groups (Allen, 2011). Some small groups are more homogenous, meaning the members are more similar, and some are more heterogeneous, meaning the members are more different. Diversity and difference within groups has advantages and disadvantages. In terms of advantages, research finds that, in general, culturally heterogeneous groups perform better than more homogenous groups (Haslett & Ruebush, 1999).
Additionally, when group members have time to get to know each other and competently communicate across their differences, the advantages of diversity include better decision making due to different perspectives (Thomas, 1999). Unfortunately, groups often operate under time constraints and other pressures that make the possibility for intercultural dialogue and understanding difficult. The main disadvantage of heterogeneous groups is the possibility for conflict, but since all groups experience conflict, this is not solely due to the presence of diversity. We will now look more specifically at how some of the cultural value orientations we have learned about already in this text can play out in groups with international diversity and how domestic diversity in terms of demographics can influence group decision making.
International Diversity in Group Interactions
Cultural value orientations such as individualism/collectivism, power distance, and high-/low-context communication styles all manifest on a continuum of communication behaviors and can influence group decision making (Yates & de Oliveira, 2016). Group members from individualistic cultures are more likely to value task-oriented, efficient, and direct communication. This could manifest in behaviors such as dividing tasks into individual projects before collaboration begins and then openly debating ideas during discussion and decision-making. Additionally, people from cultures that value individualism are more likely to express dissent from a decision, essentially expressing their disagreement with the group. Group members from collectivistic cultures are more likely to value relationships over the task. Because of this, they also tend to value conformity and face-saving (i.e., indirect) communication. This could manifest in behaviors such as establishing norms that include periods of socializing to build relationships before task-oriented communication (like negotiations) begins or norms that limit public disagreement in favor of more indirect communication that doesn’t challenge the face of other group members or the group’s leader. In a group composed of people from a collectivistic culture, each member would likely play harmonizing roles, looking for signs of conflict and resolving them before they become public.
Power distance can also affect group interactions. Some cultures rank higher on power-distance scales, meaning they value hierarchy, make decisions based on status, and believe that people have a set place in society that is unchangeable. Group members from high-power-distance cultures would likely appreciate a strong designated leader who exhibits a more directive leadership style and prefer groups in which members have clear and assigned roles. In a group that is homogenous in terms of having a high-power-distance orientation, members with higher status would be able to openly provide information, and those with lower status may not provide information unless a higher status member explicitly seeks it from them. Low-power-distance cultures do not place as much value and meaning on status and believe that all group members can participate in decision-making. Group members from low-power-distance cultures would likely freely speak their mind during a group meeting and prefer a participative leadership style.
How much meaning is conveyed through the context surrounding verbal communication can also affect group communication. Some cultures have a high-context communication style in which much of the meaning in an interaction is conveyed through context such as nonverbal cues and silence. Group members from high-context cultures may avoid saying something directly, assuming that other group members will understand the intended meaning even if the message is indirect. Therefore, if someone disagrees with a proposed course of action, he or she may say, “Let’s discuss this tomorrow,” and mean, “I don’t think we should do this.” Such indirect communication is also a face-saving strategy that is common in collectivistic cultures. Other cultures have a low-context communication style that places more importance on the meaning conveyed through words than through context or nonverbal cues. Group members from low-context cultures often say what they mean and mean what they say. For example, if someone does not like an idea, they might say, “I think we should consider more options. This one doesn’t seem like the best we can do.”
In any of these cases, an individual from one culture operating in a group with people of a different cultural orientation could adapt to the expectations of the host culture, especially if that person possesses a high degree of intercultural communication competence (ICC). Additionally, people with high ICC can also adapt to a group member with a different cultural orientation than the host culture. Even though these cultural orientations connect to values that affect our communication in consistent ways, individuals may exhibit different communication behaviors depending on their own individual communication style and the situation.
Domestic Diversity and Group Communication
While it is becoming more likely that we will interact in small groups with international diversity, we are guaranteed to interact in groups that are diverse in terms of the cultural identities found within a single country or the subcultures found within a larger cultural group.
Gender stereotypes sometimes influence the roles that people play within a group. For example, the stereotype that women are more nurturing than men may lead group members (both male and female) to expect that women will play the role of supporters or harmonizers within the group (Hentschel, Heilman, & Peus, 2019). Since women have primarily performed secretarial work since the 1900s, it may also be expected that women will play the role of recorder. In both of these cases, stereotypical notions of gender place women in roles that are typically not as valued in group communication. The opposite is true for men. In terms of leadership, despite notable exceptions, research shows that men fill an overwhelmingly disproportionate amount of leadership positions. We are socialized to see certain behaviors by men as indicative of leadership abilities, even though they may not be. For example, men are often perceived to contribute more to a group because they tend to speak first when asked a question or to fill a silence and are perceived to talk more about task-related matters than relationally oriented matters.
Both of these tendencies create a perception that men are more engaged with the task. Men are also socialized to be more competitive and self-congratulatory, meaning that their communication may be seen as dedicated and their behaviors seen as powerful, and that when their work isn’t noticed they will be more likely to make it known to the group rather than take silent credit. Even though we know that the relational elements of a group are crucial for success, even in high-performance teams, that work is not as valued in our society as the task-related work.
Despite the fact that some communication patterns and behaviors related to our typical (and stereotypical) gender socialization affect how we interact in and form perceptions of others in groups, the differences in group communication that used to be attributed to gender in early group communication research seem to be diminishing. This is likely due to the changing organizational cultures from which much group work emerges, which have now had more than sixty years to adjust to women in the workplace. It is also due to a more nuanced understanding of gender-based research, which does not take a stereotypical view from the beginning as many of the early male researchers did.
Now, instead of assuming biological sex is a factor that creates inherent communication differences, group communication scholars see that men and women both exhibit a range of behaviors that are more or less feminine or masculine. It is these gendered behaviors, and not a person’s gender, that seem to have more of an influence on perceptions of group communication. Interestingly, group interactions are still masculinist in that male and female group members prefer a more masculine communication style for task leaders and that both males and females in this role are more likely to adapt to a more masculine communication style. Conversely, men who take on social-emotional leadership behaviors adopt a more feminine communication style. In short, it seems that although masculine communication traits are more often associated with high status positions in groups, both men and women adapt to this expectation and are evaluated similarly (Haslett & Ruebush, 1999).

In terms of age, for the first time since industrialization began, it is common to have three generations of people (and sometimes four) working side by side in an organizational setting. Although four generations often worked together in early factories, they were segregated based on their age group, and a hierarchy existed with older workers at the top and younger workers at the bottom. Today, however, generations interact regularly, and it is common for an older person to have a leader or supervisor who is younger than him or her (Allen, 2011). The current generations in the US workplace and consequently in work-based groups include the following:
- The Silent Generation. Born between 1925 and 1942, currently in their mid-60s to mid-80s, this is the smallest generation in the workforce right now, as many have retired or left for other reasons. This generation includes people who were born during the Great Depression or the early part of World War II, many of whom later fought in the Korean War (Clarke, 1970).
- The Baby Boomers. Born between 1946 and 1964, currently in their late forties to mid-60s, this is the largest generation in the workforce right now. Baby boomers are the most populous generation born in US history, and they are working longer than previous generations, which means they will remain the predominant force in organizations for ten to twenty more years.
- Generation X. Born between 1965 and 1981, currently in their early thirties to mid-40s, this generation was the first to see technology like cell phones and the Internet make its way into classrooms and our daily lives. Compared to previous generations, “Gen-Xers” are more diverse in terms of race, religious beliefs, and sexual orientation and have a greater appreciation for and understanding of diversity.
- Generation Y. Born between 1982 and 2000, “Millennials” as they are also called are currently in their late teens up to about thirty years old. This generation is not as likely to remember a time without technology such as computers and cell phones. They are just entering into the workforce and have been greatly affected by recent economic crises. They are experiencing significantly high unemployment rates.
The benefits and challenges that come with diversity of group members are important to consider. Since we will all work in diverse groups, we should be prepared to address potential challenges in order to reap the benefits. Diverse groups may be wise to coordinate social interactions outside of group time in order to find common ground that can help facilitate interaction and increase group cohesion. We should be sensitive but not let sensitivity create fear of “doing something wrong” that then prevents us from having meaningful interactions.
References
Figures
Figure 13.1: Social-emotional leaders are reflective thinkers who use their perception skills to analyze group dynamics and maintain a positive climate. Dim Hou. 2019. Unsplash license. https://unsplash.com/photos/2P6Q7_uiDr0
Figure 13.2: Common components of group problems. Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0.
Figure 13.3: The group problem-solving process. Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0.
Figure 13.4: Brainstorming is a good way to generate possible solutions to a problem. Below are some suggestions to make brainstorming more of a decision-making method. Monstera. 2021. Pexels license. https://www.pexels.com/photo/excited-black-woman-using-laptop-9429552/
Figure 13.5: Culturally heterogeneous groups perform better than more homogenous groups. fauxels. 2019. Pexels license. https://www.pexels.com/photo/photo-of-people-near-wooden-table-3184418/
Figure 13.6: It is common to have different generations working together in an organizational setting. Rendy Novantino. 2021. Unsplash license. https://unsplash.com/photos/wJoRe38l8fc
Section 13.1
Benne, K. D., & Sheats, P. (1948). Functional roles of group members. Journal of Social Issues 4(2), 41–49. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-4560.1948.tb01783.x
Bormann, E. G., & Bormann, N.C., (1988). Effective small group communication (4th ed.). Burgess International Group.
Burke, C. S., Georganta, E., & Marlow, S. (2019). A bottom up perspective to understanding the dynamics of team roles in mission critical teams. Frontiers in psychology, 10, 1322. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01322
Cragan, J. F., & Wright, D. W. (1991). Communication in small group discussions: An integrated approach (3rd ed.). West Publishing.
Koch, A. (2013, October 24). Individual roles in groups. https://prezi.com/gmbfihtzyjg4/individual-roles-in-groups/
Pavitt, C. (1999). Theorizing about the group communication-leadership relationship. In L. R. Frey (Ed.), The handbook of group communication Theory and research (pp. 313-334). Sage.
Section 13.2
Adams, K., and Galanes, G. (2009). Communicating in groups: Applications and skills (7th ed.). McGraw Hill.
Allen, B. J. (2011). Difference matters: Communicating social identity (2nd ed.). Waveland Press.
Bormann, E. G., & Bormann, N.C., (1988). Effective small group communication (4th ed.). Burgess International Group.
Clarke, G. (1970, June 29). The silent generation revisited. Time, 95(26), 38-40.
Cragan, J. F., & Wright, D. W. (1991). Communication in small group discussions: An integrated approach (3rd ed.). West Publishing.
Delbecq, A. L., & Van de Ven, A. H. (1971). A group process model for problem identification and program planning. The Journal of Applied Behavioral Science, 7(4), 466–492. https://doi.org/10.1177/002188637100700404
Franken, I. H. A., and Muris, P. (2005). Individual differences in decision-making. Personality and Individual Differences, 39(5), 991–998. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2005.04.004
Haslett, B.B., Ruebush, J. (1999). What differences do individual differences in groups make? The effects of individuals, culture, and group composition. In L. R. Frey, D. S. Gouran, & M. S. Poole (Eds.), The handbook of group communication theory and research (pp. 115–138). Sage.
Hentschel, T., Heilman, M. E., & Peus, C. V. (2019). The multiple dimensions of gender stereotypes: A current look at men’s and women’s characterizations of others and themselves. Frontiers in Psychology, 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00011
Napier, R. W., & Gershenfeld, M. K. (2004). Groups: Theory and experience (7th ed.). Houghton Mifflin.
Osborn, A. F. (1959). Applied imagination. Charles Scribner’s Sons.
Schippers, M. C., & Rus, D. C. (2021). Majority decision-making works best under conditions of leadership ambiguity and shared task representations. Frontiers in Psychology, 12, 519295. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.519295
Stanton, C. (2009, November 3). How to deliver group presentations: The unified team approach. http://sixminutes.dlugan.com/group-presentations-unified-team-approach/
Thomas, D. C. (1999). Cultural diversity and work group effectiveness: An experimental study. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology 30(2), 242–263. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022022199030002006
Yates, J. F., & de Oliveira, S. (2016). Culture and decision making. Organizational behavior and human decision processes, 136, 106–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.obhdp.2016.05.003
A task-related role that functions to keep the group on track toward completing its task by managing the agenda and setting and assessing goals in order to monitor the group’s progress
This role includes behaviors that are more evenly shared compared to other roles, as ideally, all group members present new ideas, initiate discussions of new topics, and contribute their own relevant knowledge and experiences
The person who has this task-related role asks for more information, elaboration, or clarification on items relevant to the group’s task
This person manages the flow of conversation in a group in order to achieve an appropriate balance so that all group members get to participate in a meaningful way
The person who takes notes on the discussion and activities that occur during a group meeting. This role is the only role that is limited to one person at a time
A maintenance role that is characterized by communication behaviors that encourage other group members and provide emotional support as needed
Group members who help manage the various types of group conflict that emerge during group communication, they keep their eyes and ears open for signs of conflict among group members and ideally intervene before it escalates
This person helps manage the diversity within a group by mediating intercultural conflict, articulating common ground between different people, and generally creating a climate where difference is seen as an opportunity rather than as something to be feared
A group member who makes excessive verbal contributions preventing equal participation by other group members. Can include the “egghead” and the “stage hog.”
This technique guides decision making through a four-step process that includes idea generation and evaluation and seeks to elicit equal contributions from all group members
A commonly used decision-making technique in which a majority (one-half plus one) must agree before making the decision
A decision making technique in which a designated authority or expert has final say over a decision and may or may not consider the input of other group members
A decision-making technique in which all members of the group must agree on the same decision

