3 Language and Meaning
Introduction
The relationship between language and meaning is not a straightforward one. One reason for this complicated relationship is the limitlessness of modern language systems like English (Crystal, 2005). Language is productive in the sense that there are an infinite number of utterances we can make by connecting existing words in new ways. In addition, there is no limit to a language’s vocabulary, as new words are coined daily. Of course, words aren’t the only things we need to communicate, and although verbal and nonverbal communication are closely related in terms of how we make meaning, nonverbal communication is not productive and limitless. Although we can only make a few hundred physical signs, we have about a million words in the English language. So with all this possibility, how does communication generate meaning?
We arrive at meaning through the interaction between our nervous and sensory systems and some stimulus outside of them. It is here, between what the communication models labeled as encoding and decoding, that meaning is generated as sensory information is interpreted. The indirect and sometimes complicated relationship between language and meaning can lead to confusion, frustration, or even humor. We may even experience a little of all three, when we stop to think about how there are some twenty-five definitions available to tell us the meaning of word meaning! (Crystal, 2005) Since language and symbols are the primary vehicle for our communication, it is important that we not take the components of our verbal communication for granted.
3.1 Language is Symbolic
Our language system is primarily made up of symbols. A symbol is something that stands in for or represents something else. Symbols can be communicated verbally (speaking the word hello), in writing (putting the letters H-E-L-L-O together), or nonverbally (waving your hand back and forth). In any case, the symbols we use stand in for something else, like a physical object or an idea, they do not actually correspond to the thing being referenced in any direct way.
The symbols we use combine to form language systems or codes. Codes are culturally agreed on and ever-changing systems of symbols that help us organize, understand, and generate meaning (Leeds-Hurwitz, 1993). There are about 6,000 language codes used in the world, and around 40 percent of those (2,400) are only spoken and do not have a written version (Crystal, 2005).
The symbolic nature of our communication is a quality unique to humans. Since the words we use do not have to correspond directly to a “thing” in our “reality,” we can communicate in abstractions. This property of language is called displacement. It refers to our ability to talk about events that are removed in space or time from a speaker and situation (Crystal, 2005).
For example, the word calculate comes from the Latin word calculus, which means “pebble.” However, what does a pebble have to do with calculations? Pebbles were used, very long ago, to calculate things before we developed verbal or written numbering systems (Hayakawa & Hayakawa, 1990). As I noted earlier, a farmer may have kept, in a box, one pebble for each of his chickens. Each pebble represented one chicken, meaning that each symbol (the pebble) had a direct correlation to another thing out in the world (its chicken). This system allowed the farmer to keep track of his livestock. He could periodically verify that each pebble had a corresponding chicken. If there was a discrepancy, he would know that a chicken was lost, stolen, or killed.
Later, symbols were developed that made accounting a little easier. Instead of keeping track of boxes of pebbles, the farmer could record a symbol like the word five or the numeral 15 that could stand in for five or fifteen pebbles. This demonstrates how our symbols have evolved and how some still carry that ancient history with them, even though we are unaware of it. While this evolution made communication easier in some ways, it also opened up room for misunderstanding, since the relationship between symbols and the objects or ideas they represented became less straightforward. Although the root of calculate means “pebble,” the word calculate today has at least six common definitions.
The Triangle of Meaning
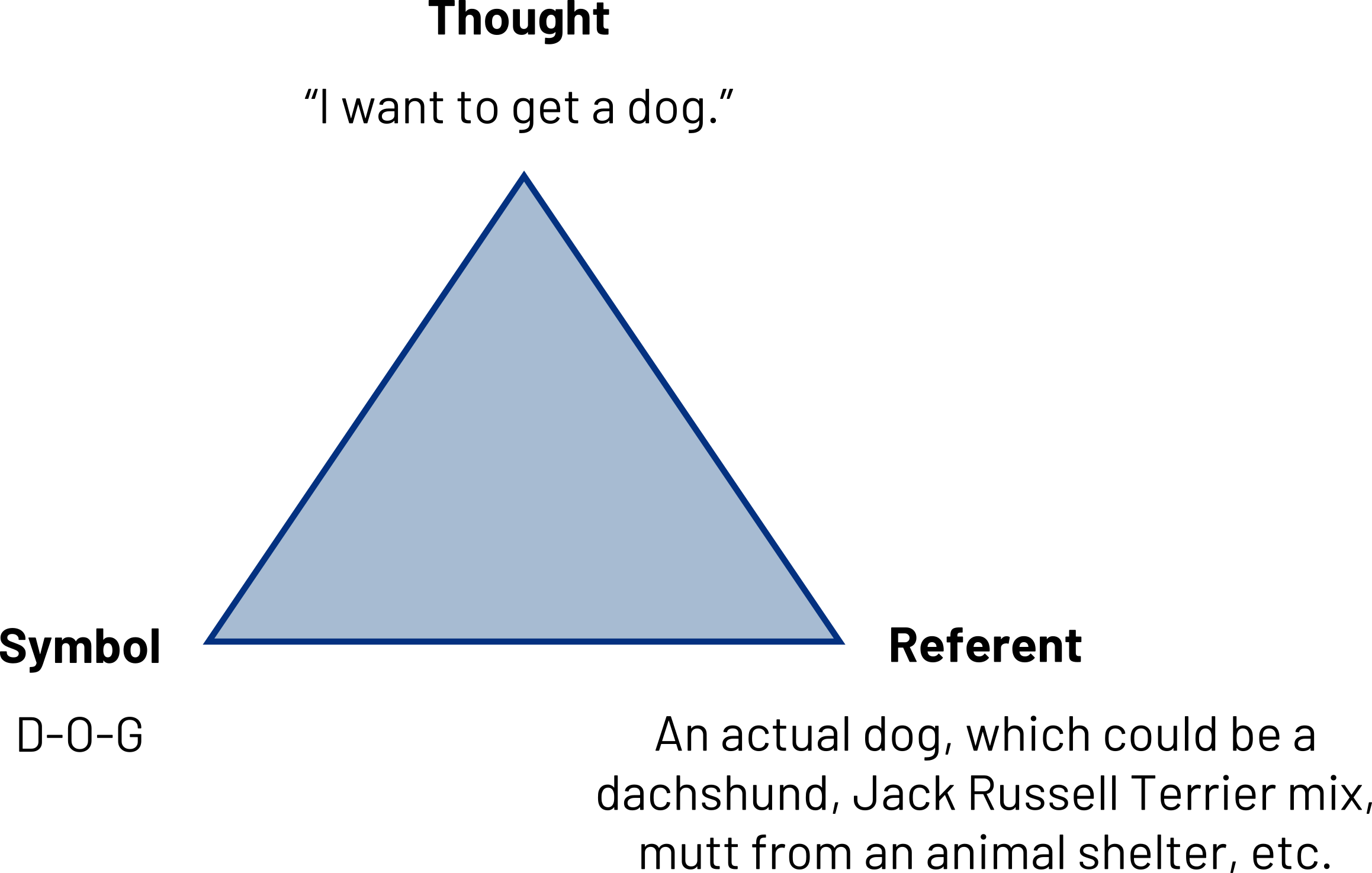
The triangle of meaning is a model of communication that indicates the relationship among a thought, symbol, and referent and highlights the indirect relationship between the symbol and referent (Ogden & Richards, 1923). As you can see in figure 3.1 “Triangle of meaning," the thought is the concept or idea a person references. The symbol is the word that represents the thought, and the referent is the object or idea to which the symbol refers.
This model is useful for us as communicators because when we are aware of the indirect relationship between symbols and referents, we are aware of how common misunderstandings occur, as the following example illustrates. Jasper and Abby have been thinking about getting a new dog. So each of them is having a similar thought. They are each using the same symbol, the word dog, to communicate about their thought. Their referents, however, are different. Jasper is thinking about a small dog like a dachshund, and Abby is thinking about an Australian shepherd. Since the word dog does not refer to one specific object in our reality, it is possible for them to have the same thought and use the same symbol only to find out the other person did not have the same thing in mind.
Being aware of this indirect relationship between symbol and referent, we can try to compensate for it by getting clarification. Abby might ask Jasper, “What kind of dog do you have in mind?” This question would allow Jasper to describe his referent, which would allow for more shared understanding. If Jasper responds, “Well, I like short-haired dogs. And we need a dog that will work well in an apartment,” then there is still quite a range of referents. Abby could ask questions for clarification, like “Sounds like you’re saying that a smaller dog might be better. Is that right?” Getting to a place of shared understanding can be difficult, even when we define our symbols and describe our referents.
Definitions
Definitions help us narrow the meaning of particular symbols, which also narrows a symbol’s possible referents. They also provide more words (symbols) for which we must determine a referent.
Words have denotative and connotative meanings. Denotation refers to definitions that are accepted by the language group as a whole, or the dictionary definition of a word. For example, the denotation of the word cowboy is a man who takes care of cattle. Another denotation is a reckless and/or independent person. A more abstract word, like change, would be more difficult to understand due to the multiple denotations.
Connotation refers to definitions that are based on emotion- or experience-based associations people have with a word. To go back to our previous words, change can have positive or negative connotations depending on a person’s experiences. A person who just ended a long-term relationship may think of change as good or bad depending on what he or she thought about his or her former partner. Even words like handkerchief that only have one denotation can have multiple connotations. A handkerchief can conjure up thoughts of dainty Southern belles or disgusting snot-rags.
A word like cowboy has many connotations, and philosophers of language have explored how connotations extend beyond one or two experiential or emotional meanings of a word to constitute cultural myths (Barthes, 1972). Cowboy, for example, connects to the frontier and the western history of the United States, which has mythologies associated with it that help shape the narrative of the nation. While people who grew up with cattle or have family that ranch may have a very specific connotation of the word cowboy based on personal experience, other people’s connotations may be more influenced by popular cultural symbolism like that seen in westerns.
Language is Learned
As we just learned, the relationship between the symbols that make up our language and their referents is arbitrary, which means they have no meaning until we assign it to them. In order to use a language effectively system, we have to learn, over time, which symbols go with which referents, since we cannot just tell by looking at the symbol. Like me, you probably learned what the word apple meant by looking at the letters A-P-P-L-E and a picture of an apple and having a teacher or caregiver help you sound out the letters until you said the whole word. Over time, we associated that combination of letters with the picture of the red delicious apple and no longer had to sound each letter out. This is a deliberate process that may seem slow in the moment, but as we will see next, our ability to acquire language is actually quite astounding. We did not just learn individual words and their meanings, though; we also learned rules of grammar that help us put those words into meaningful sentences.
The Rules of Language
Any language system has to have rules to make it learnable and usable. Grammar refers to the rules that govern how words are used to make phrases and sentences. Someone would likely know what you mean by the question “Where’s the remote control?” But “The control remote where’s?” is likely to be unintelligible or at least confusing (Crystal, 2005). Knowing the rules of grammar is important in order to be able to write and speak to be understood, but knowing these rules is not enough to make you an effective communicator. As we will learn later, creativity and play also have a role in effective verbal communication. Even though teachers have long enforced the idea that there are right and wrong ways to write and say words, there really is not anything inherently right or wrong about the individual choices we make in our language use. Rather, it is our collective agreement that gives power to the rules that govern language.
Looking back to our discussion of connotation, we can see how individuals play a role in how meaning and language are related, since we each bring our own emotional and experiential associations with a word that are often more meaningful than a dictionary definition. In addition, we have quite a bit of room for creativity, play, and resistance with the symbols we use. Have you ever had a secret code with a friend that only you knew? This can allow you to use a code word in a public place to get meaning across to the other person who is “in the know” without anyone else understanding the message. The fact that you can take a word, give it another meaning, have someone else agree on that meaning, and then use the word in your own fashion clearly shows that meaning is in people rather than words. As we will learn later, many slang words developed because people wanted a covert way to talk about certain topics like drugs or sex without outsiders catching on.
Language is Expressive Functions of Language
What utterances make up our daily verbal communication? Some of our words convey meaning, some convey emotions, and some actually produce actions. Language also provides endless opportunities for fun because of its limitless, sometimes nonsensical, and always changing nature. In this section, we will learn about the five functions of language, which show us that language is expressive, language is powerful, language is fun, language is dynamic, and language is relational.
Language is Expressive
Verbal communication helps us meet various needs through our ability to express ourselves. In terms of instrumental needs, we use verbal communication to ask questions that provide us with specific information. We also use verbal communication to describe things, people, and ideas. Verbal communication helps us inform, persuade, and entertain others, which as we will learn later are the three general purposes of public speaking. It is also through our verbal expressions that our personal relationships are formed. At its essence, language is expressive. Verbal expressions help us communicate our observations, thoughts, feelings, and needs (McKay, Davis, & Fanning, 1995).
Expressing Observations
When we express observations, we report on the sensory information we are taking or have taken in. Eyewitness testimony is a good example of communicating observations. Witnesses are not supposed to make judgments or offer conclusions; they only communicate factual knowledge as they experienced it. For example, a witness could say, “I saw a white Mitsubishi Eclipse leaving my neighbor’s house at 10:30 pm.” Observation and description occur in the first step of the perception-checking process. When you are trying to make sense of an experience, expressing observations in a descriptive rather than evaluative way can lessen defensiveness, which facilitates competent communication.
Expressing Thoughts
When we express thoughts, we draw conclusions based on what we have experienced. In the perception process, this is similar to the interpretation step. We take various observations and evaluate and interpret them to assign them meaning (a conclusion). Whereas our observations are based on sensory information (what we saw, what we read, what we heard), thoughts are connected to our beliefs (what we think is true/false), attitudes (what we like and dislike), and values (what we think is right/wrong or good/bad). Jury members are expected to express thoughts based on reported observations to help reach a conclusion about someone’s guilt or innocence. A juror might express the following thought: “The neighbor who saw the car leaving the night of the crime seemed credible. And the defendant seemed to have a shady past—I think he’s trying to hide something.” Sometimes people intentionally or unintentionally express thoughts as if they were feelings. For example, when people say, “I feel like you’re too strict with your attendance policy,” they are not really expressing a feeling; they are expressing a judgment about the other person (a thought).
Expressing Feelings
When we express feelings, we communicate our emotions. Expressing feelings is a difficult part of verbal communication, because there are many social norms about how, why, when, where, and to whom we express our emotions. Norms for emotional expression also vary based on nationality and other cultural identities and characteristics such as age and gender. In terms of age, young children are typically freer to express positive and negative emotions in public. Gendered elements intersect with age as boys grow older and are socialized into a norm of emotional restraint. Although individual men vary in the degree to which they are emotionally expressive, a prevailing social norm encourages and expects women to be more emotionally expressive than men.
Expressing feelings can be uncomfortable for those listening. Some people are generally not good at or comfortable with receiving and processing other people’s feelings. Even those with good empathetic listening skills can be positively or negatively affected by others’ emotions. Expressions of anger can be especially difficult to manage because they represent a threat to the face and self-esteem of others.
Despite the fact that expressing feelings is more complicated than other forms of expression, emotion sharing is an important part of how we create social bonds and empathize with others, and it can be improved.
In order to express our emotions, it is important that we develop an emotional vocabulary. The more specific we can be when we are verbally communicating our emotions, the less ambiguous our emotions will be for the person decoding our message. As we expand our emotional vocabulary, we are able to convey the intensity of the emotion we are feeling whether it is mild, moderate, or intense. For example, happy is mild, delighted is moderate, and ecstatic is intense; ignored is mild, rejected is moderate, and abandoned is intense (Hargie, 2011).
In a time when so much of our communication is electronically mediated, it is likely that we will communicate emotions through the written word in an e-mail, text, or instant message. We may also still use pen and paper when sending someone a thank-you note, a birthday card, or a sympathy card. Communicating emotions through the written (or typed) word can have advantages such as time to compose your thoughts and convey the details of what you are feeling. There are also disadvantages in that important context and nonverbal communication cannot be included. Things like facial expressions and tone of voice offer much insight into emotions that may not be expressed verbally. There is also a lack of immediate feedback. Sometimes people respond immediately to a text or e-mail, but think about how frustrating it is when you text someone and they do not get back to you right away. If you are in need of emotional support or want validation of an emotional message you just sent, waiting for a response could end up negatively affecting your emotional state.
Expressing Needs
When we express needs, we are communicating in an instrumental way to help us get things done. Since we usually know our needs more than others do, it is important for us to be able to convey those needs to others. Expressing needs can help us get a project done at work or help us navigate the changes of a long-term romantic partnership. Not expressing needs can lead to feelings of abandonment, frustration, or resentment. For example, if one romantic partner expresses the following thought “I think we’re moving too quickly in our relationship” but does not also express a need, the other person in the relationship does not have a guide for what to do in response to the expressed thought. Stating, “I need to spend some time with my hometown friends this weekend. Would you mind if I went home by myself?” would likely make the expression more effective. Be cautious of letting evaluations or judgments sneak into your expressions of need. Saying, “I need you to stop suffocating me!” really expresses a thought-feeling mixture more than a need.
[table id=1 /]
Language Is Powerful
The contemporary American philosopher David Abram wrote, “Only if words are felt, bodily presences, like echoes or waterfalls, can we understand the power of spoken language to influence, alter, and transform the perceptual world” (Abram, 1997). This statement encapsulates many of the powerful features of language. Next, we will discuss how language expresses our identities, affects our credibility, serves as a means of control, and performs actions.
Language Expresses our Identities
The power of language to express our identities varies depending on the origin of the label (self-chosen or other imposed) and the context. People are usually comfortable with the language they use to describe their own identities but may have issues with the labels others place on them. In terms of context, many people express their “Irish” identity on St. Patrick’s Day, but they may not think much about it over the rest of the year. There are many examples of people who have taken a label that was imposed on them, one that usually has negative connotations, and intentionally used it in ways that counter previous meanings. Some country music singers and comedians have reclaimed the label redneck, using it as an identity marker they are proud of rather than a pejorative term. Other examples of people reclaiming identity labels is the “black is beautiful” movement of the 1960s that repositioned black as a positive identity marker for African Americans and the “queer” movement of the 1980s and ’90s that reclaimed queer as a positive identity marker for some gay, lesbian, bisexual, and transgender people. Even though some people embrace reclaimed words, they still carry their negative connotations and are not openly accepted by everyone.
Language Affects our Credibility
One of the goals of this chapter is to help you be more competent with your verbal communication. People make assumptions about your credibility based on how you speak and what you say. Even though we have learned that meaning is in people rather than words and that the rules that govern verbal communication, like rules of grammar, are arbitrary, these norms still mean something. You do not have to be a perfect grammarian to be perceived as credible. In fact, if you followed the grammar rules for written communication to the letter you would actually sound strange, since our typical way of speaking is not as formal and structured as writing. However, you still have to support your ideas and explain the conclusions you make to be seen as competent. You have to use language clearly and be accountable for what you say in order to be seen as trustworthy. Using informal language and breaking social norms we have discussed so far would not enhance your credibility during a professional job interview, but it might with your friends at a tailgate party. Politicians know that the way they speak affects their credibility, but they also know that using words that are too scientific or academic can lead people to perceive them as eggheads, which would hurt their credibility. Politicians and many others in leadership positions need to be able to use language to put people at ease, relate to others, and still appear confident and competent.
Language is a Means of Control
Control is a word that has negative connotations, but our use of it here can be positive, neutral, or negative. Verbal communication can be used to reward and punish. We can offer verbal communication in the form of positive reinforcement to praise someone. We can withhold verbal communication or use it in a critical, aggressive, or hurtful way as a form of negative reinforcement.
Directives are utterances that try to get another person to do something. They can range from a rather polite ask or request to a more forceful command or insist. Context informs when and how we express directives and how people respond to them. Promises are often paired with directives in order to persuade people to comply, and those promises, whether implied or stated, should be kept in order to be an ethical communicator. Keep this in mind to avoid arousing false expectations on the part of the other person (Hayakawa & Hayakawa, 1990).
Rather than verbal communication being directed at one person as a means of control, the way we talk creates overall climates of communication that may control many. Verbal communication characterized by empathy, understanding, respect, and honesty creates open climates that lead to more collaboration and more information exchange. Verbal communication that is controlling, deceitful, and vague creates a closed climate in which people are less willing to communicate and less trusting (Brown, 2006).
Language is Dynamic
As we already learned, language is essentially limitless. We may create a one-of-a-kind sentence combining words in new ways and never know it. Aside from the endless structural possibilities, words change meaning, and new words are created daily. In this section, we will learn more about the dynamic nature of language by focusing on neologisms and slang.
Neologisms
Neologisms are newly coined or used words. Newly coined words are those that were just brought into linguistic existence. Newly used words make their way into languages in several ways, including borrowing and changing structure. Taking is actually a more fitting descriptor than borrowing, since we take words but do not really give them back. In any case, borrowing is the primary means through which languages expand. English is a good case in point. Most of its vocabulary is borrowed and does not reflect the language’s Germanic origins. English has been called the “vacuum cleaner of languages” (Crystal, 2005). Weekend is a popular English word based on the number of languages that have borrowed it. We have borrowed many words, like chic from French, karaoke from Japanese, and caravan from Arabic.

Existing words also change in their use and meaning. The digital age has given rise to some interesting changes in word usage. Before Facebook, the word friend had many meanings, but it was mostly used as a noun referring to a companion. The sentence, I’ll friend you, would not have made sense to many people just a few years ago because friend was not used as a verb. Google went from being a proper noun referring to the company to a more general verb that refers to searching for something on the Internet (perhaps not even using the Google search engine). Meanings can expand or contract without changing from a noun to a verb. Gay, an adjective for feeling happy, expanded to include gay as an adjective describing a person’s sexual orientation. Perhaps because of the confusion that this caused, the meaning of gay has contracted again, as the earlier meaning is now considered archaic, meaning it is no longer in common usage.
Slang
Slang is a great example of the dynamic nature of language. Slang refers to new or adapted words that are specific to a group, context, and/or time period; regarded as less formal; and representative of people’s creative play with language. Research has shown that only about 10 percent of the slang terms that emerge over a fifteen-year period survive. Many more take their place though, as new slang words are created using inversion, reduction, or old-fashioned creativity (Allan & Burridge, 2006).
Inversion is a form of word play that produces slang words like sick, wicked, and bad that refer to the opposite of their typical meaning. Reduction creates slang words such as pic, sec, and later from picture, second, and see you later. New slang words often represent what is edgy, current, or simply relevant to the daily lives of a group of people. Many creative examples of slang refer to illegal or socially taboo topics like sex, drinking, and drugs. It makes sense that developing an alternative way to identify drugs or talk about taboo topics could make life easier for the people who partake in such activities. Slang allows people who are in “in the know” to break the code and presents a linguistic barrier for unwanted outsiders. Taking a moment to think about the amount of slang that refers to being intoxicated on drugs or alcohol or engaging in sexual activity should generate a lengthy list.
Language is Relational
We use verbal communication to initiate, maintain, and terminate our interpersonal relationships. The first few exchanges with a potential romantic partner or friend help us size the other person up and figure out if we want to pursue a relationship or not. We then use verbal communication to remind others how we feel about them and to check in with them—engaging in relationship maintenance through language use. When negative feelings arrive and persist, or for many other reasons, we often use verbal communication to end a relationship.
Language Can Bring Us Together
Interpersonally, verbal communication is key to bringing people together and maintaining relationships. Whether intentionally or unintentionally, our use of words like I, you, we, our, and us affect our relationships. “We language” includes the words we, our, and us and can be used to promote a feeling of inclusiveness. “I language” can be useful when expressing thoughts, needs, and feelings because it leads us to “own” our expressions and avoid the tendency to mistakenly attribute the cause of our thoughts, needs, and feelings to others. Communicating emotions using “I language” may also facilitate emotion sharing by not making our conversational partner feel at fault or defensive. For example, instead of saying, “You’re making me crazy!” you could say, “I’m starting to feel really anxious because we can’t make a decision about this.” Conversely, “you language” can lead people to become defensive and feel attacked, which could be divisive and result in feelings of interpersonal separation.

Aside from the specific words that we use, the frequency of communication affects relationships. Of course, the content of what is said is important, but research shows that romantic partners who communicate frequently with each other and with mutual friends and family members experience less stress and uncertainty in their relationship and are more likely to stay together (McCornack, 2007).
When frequent communication combines with supportive messages, which are messages communicated in an open, honest, and non-confrontational way, people are sure to come together.
Language Can Separate Us
Whether its criticism, teasing, or language differences, verbal communication can also lead to feelings of separation. Language differences alone do not present insurmountable barriers. We can learn other languages with time and effort, there are other people who can translate and serve as bridges across languages, and we can communicate quite a lot nonverbally in the absence of linguistic compatibility. People who speak the same language can intentionally use language to separate. The words us and them can be a powerful start to separation.

Think of how language played a role in segregation in the United States as the Supreme Court upheld the notion of “separate but equal” and how apartheid affected South Africa as limits, based on finances and education, were placed on the black majority’s rights to vote. Symbols, both words and images, were a very important part of Hitler’s rise to power in the 1930s and ’40s in Europe. Various combinations of colored stars, triangles, letters, and other symbols were sewn onto the clothing or uniforms of people persecuted by the Nazis in order to classify them. People were labeled and reduced to certain characteristics rather than seen as complete humans, which facilitated the Nazis’ oppression, violence, and killing (Holocaust and Human Rights Education Center,2012).
At the interpersonal level, unsupportive messages can make others respond defensively, which can lead to feelings of separation and actual separation or dissolution of a relationship. It is impossible to be supportive in our communication all the time, but consistently unsupportive messages can hurt others’ self-esteem, escalate conflict, and lead to defensiveness. People who regularly use unsupportive messages may create a toxic win/lose climate in a relationship. Six verbal tactics that can lead to feelings of defensiveness and separation are global labels, sarcasm, dragging up the past, negative comparisons, judgmental “you” messages, and threats (McKay, Davis, & Fanning, 1995).
Common Types of Unsupportive Messages
- Global labels. “You’re a liar.” Labeling someone irresponsible, untrustworthy, selfish, or lazy calls his or her whole identity as a person into question. Such sweeping judgments and generalizations are sure to escalate a negative situation.
- Sarcasm. “No, you didn’t miss anything in class on Wednesday. We just sat here and looked at each other.” Even though sarcasm is often disguised as humor, it usually represents passive-aggressive behavior through which a person indirectly communicates negative feelings.
- Dragging up the past. “I should have known not to trust you when you never paid me back that $100 I let you borrow.” Bringing up negative past experiences is a tactic used by people when they do not want to discuss a current situation. Sometimes people have built up negative feelings that are suddenly let out by a seemingly small thing in the moment.
- Negative comparisons. “Jade graduated from college without any credit card debt. I guess you’re just not as responsible as her.” Holding a person up to the supposed standards or characteristics of another person can lead to feelings of inferiority and resentment. Parents and teachers may unfairly compare children to their siblings.
- Judgmental “you” messages. “You’re never going to be able to hold down a job.” Accusatory messages are usually generalized overstatements about another person that go beyond labeling but still do not describe specific behavior in a productive way.
- Threats. “If you don’t stop texting back and forth with your ex, both of you are going to regret it.” Threatening someone with violence or some other negative consequence usually signals the end of productive communication. Aside from the potential legal consequences, threats usually overcompensate for a person’s insecurity.
3.2 Using Words Well
Have you ever gotten lost because someone gave you directions that did not make sense to you? Have you ever puzzled over the instructions for how to put something like a bookshelf or grill together? When people do not use words well, there are consequences that range from mild annoyance to legal actions. When people do use words well, they can be inspiring and make us better people. In this section, we will learn how to use words well by using words clearly, using words affectively, and using words ethically.
Using Words Clearly
The level of clarity with which we speak varies depending on whom we talk to, the situation we are in, and our own intentions and motives. We sometimes make a deliberate effort to speak as clearly as possible. We can indicate this concern for clarity nonverbally by slowing our rate and increasing our volume or verbally by saying, “Frankly…” or “Let me be clear…” Sometimes it can be difficult to speak clearly—for example, when we are speaking about something with which we are unfamiliar. Emotions and distractions can also interfere with our clarity. Being aware of the varying levels of abstraction within language can help us create clearer and more “whole” messages.
Level of Abstraction
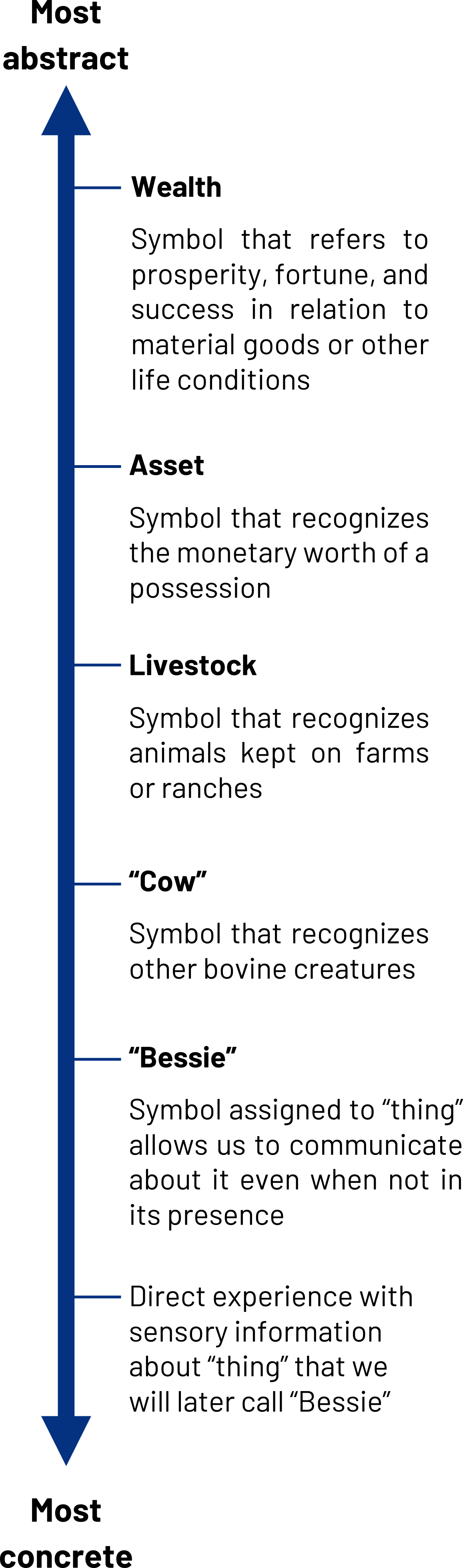
The ladder of abstraction is a model used to illustrate how language can range from concrete to abstract. As we follow a concept up the ladder of abstraction, more and more of the “essence” of the original object is lost or left out, which leaves more room for interpretation, which can lead to misunderstanding. This process of abstracting, of leaving things out, allows us to communicate more effectively because it serves as a shorthand that keeps us from having a completely unmanageable language filled with millions of words—each referring to one specific thing (Hayakawa & Hayakawa, 1990). However, it requires us to use context and other words to generate shared meaning. Some words are more directly related to a concept or idea than others are. If I asked you to go take a picture of a book, you could do that. If I asked you to go and take a picture of “work,” you couldn’t because work is an abstract word that was developed to refer to any number of possibilities from the act of writing a book, to repairing an air conditioner, to fertilizing an organic garden. You could take a picture of any of those things, but you cannot take a picture of “work.”
You can see the semanticist S. I. Hayakawa’s classic example of the abstraction ladder with "Bessie the cow" in figure 3.5 “Ladder of abstraction” (Hayakawa & Hayakawa, 1990). At the lowest level, we have something that is very concrete. At this level, we are actually in the moment of experiencing the stimuli that is coming in through our senses. We perceive the actual “thing,” which is the “cow” in front of us (either in person or as an image). This is concrete, because it is unmediated, meaning it is actually the moment of experience. As we move up a level, we give the experience a name—we are looking at “Bessie.” So now, instead of the direct experience with the “thing” in front of us, we have given the thing a name, which takes us one step away from the direct experience to the use of a more abstract symbol. Now we can talk and think about Bessie even when we are not directly experiencing her. At the next level, the word cow now lumps Bessie in with other bovine creatures that share similar characteristics. As we go on up the ladder, cow becomes livestock, livestock becomes an asset, and then an asset becomes wealth. Note that it becomes increasingly difficult to define the meaning of the symbol as we go up the ladder. With each step, we lose more of the characteristics of the original concrete experience.
When shared referents are important, we should try to use language that is lower on the ladder of abstraction. Being intentionally concrete is useful when giving directions, for example, and can help prevent misunderstanding. We sometimes intentionally use abstract language. Since abstract language is often unclear or vague, we can use it as a means of testing out a potential topic (like asking a favor), offering negative feedback indirectly (to avoid hurting someone’s feelings or to hint), or avoiding the specifics of a topic.
Definitions and Clarity
Knowing more about the role that abstraction plays in the generation of meaning can help us better describe and define the words we use. As we learned earlier, denotative definitions are those found in the dictionary—the official or agreed-on definition. Since definitions are composed of other words, people who compile dictionaries take for granted that there is a certain amount of familiarity with the words used to define another word—otherwise we would just be going in circles.
One challenge we face when defining words is our tendency to go up the ladder of abstraction rather than down (Hayakawa & Hayakawa, 1990). For example, if asked to define the word blue, you would likely say it is a color. If asked what a color is, you would say it is a tint or characteristic of the appearance of a particular thing. To define more clearly, by going down the ladder of abstraction, you could say, “It’s the color of Frank Sinatra’s eyes,” or “It’s what the sky looks like on a clear day.” People often come to understanding more quickly when a definition is descriptive and/or ties into their personal experiences. Definitions are not useless, but they are usually best when paired with examples.
Jargon refers to specialized words used by a certain group or profession. Since jargon is specialized, it is often difficult to relate to a diverse audience and should therefore be limited when speaking to people from outside the group—or at least be clearly defined when it is used.
Using Words Affectively
Affective language refers to language used to express a person’s feelings and create similar feelings in another person (Hayakawa & Hayakawa, 1990). Affective language can be intentionally used in relational contexts to create or enhance interpersonal bonds and can be effectively employed in public speaking to engage an audience and motivate them in particular ways. We also use affective language spontaneously and less intentionally. People who “speak from the heart” connect well with others due to the affective nature of their words. Sometimes people become so filled with emotion that they have to express it, and these exclamations usually arouse emotions in others. Hearing someone exclaim, “I’m so happy!” can evoke similar feelings of joy, while hearing someone exclaim, “Why me!?” while sobbing conjures up similar feelings of sadness and frustration. There are also specific linguistic devices that facilitate affective communication.
Figurative Language
When people say something is a “figure of speech,” they are referring to a word or phrase that deviates from expectations in some way in meaning or usage (Yaguello, 1998). Figurative language is the result of breaking semantic rules, but in a way that typically enhances meaning or understanding rather than diminishes it. To understand figurative language, a person has to be familiar with the semantic rules of a language and with social norms and patterns within a cultural and/or language group, which makes it difficult for nonnative speakers to grasp. Figurative language has the ability to convey much meaning in fewer words, because some of the meaning lies in the context of usage (what a listener can imply by the deviation from semantic norms) and in the listener (how the listener makes meaning by connecting the figurative language to his or her personal experience). Some examples of figurative speech include simile, metaphor, and personification.
A simile is a direct comparison of two things using the words like or as. Similes can be very explicit for conveying a specific meaning and can help increase clarity and lead people to connect personally to a meaning since they have to visualize the comparison in their mind. For example, Forrest Gump’s famous simile, “Life is like a box of chocolates. You never know what you’re gonna get,” conjures up feelings of uncertainty and excitement. More direct similes like “I slept like a baby” and “That bread was hard as a rock” do not necessarily stir the imagination but still offer an alternative way of expressing something.
A metaphor is an implicit comparison of two things that are not alike and/or are not typically associated. They become meaningful as people realize the speaker’s purpose for relating the two seemingly disparate ideas. Metaphors are figurative devices that can make our writing and speaking richer, but they require a person to balance creative associations among ideas with the common rules of the language if people are expected to figure out the meaning behind the association. A speaker must have the linguistic knowledge and insight to realize when a nonliteral use of words or ideas will be more meaningful than a literal and conventional use of those words. Metaphors challenge the imagination, which can cause each person to make sense of the metaphor in his or her own way (Olbricht, 1968).
Many metaphors spring from our everyday experiences. For example, many objects have been implicitly compared to human body parts; for example, we say a clock has hands and a face. Personification refers to the attribution of human qualities or characteristics of other living things to nonhuman objects or abstract concepts. This can be useful when trying to make something abstract more concrete and can create a sense of urgency or “realness” out of something that is hard for people to conceive. Personification has been used successfully in public awareness campaigns because it allows people to identify with something they think might not be relevant to them.
Evocative Language
Vivid language captures people’s attention and their imagination by conveying emotions and action. Think of the array of mental images that a poem or a well-told story from a friend can conjure up. Evocative language can also lead us to have physical reactions. Words like shiver and heartbroken can lead people to remember previous physical sensations related to the word. As a speaker, there may be times when evoking a positive or negative reaction could be beneficial. Evoking a sense of calm could help you talk a friend through troubling health news. Evoking a sense of agitation and anger could help you motivate an audience to action. When we are conversing with a friend or speaking to an audience, we are primarily engaging others’ visual and auditory senses. Evocative language can help your conversational partner or audience members feel, smell, or taste something as well as hear it and see it. Good writers know how to use words effectively and affectively. A well-written story, whether it is a book or screenplay, will contain all the previous elements. The rich fantasy worlds conceived in Star Trek, The Lord of the Rings, Twilight, and Harry Potter show the power of figurative and evocative language to capture our attention and our imagination.
Some words are so evocative that their usage violates the social norms of appropriate conversations. Although we could use such words to shock people, we can also use euphemisms, or less evocative synonyms for or indirect references to words or ideas that are deemed inappropriate to discuss directly. We have many euphemisms for things like excretory acts, sex, and death (Allan & Burridge, 2006). While euphemisms can be socially useful and creative, they can also lead to misunderstanding and problems in cases where communication that is more direct is warranted despite social conventions.
Using Words Ethically
Communication is irreversible. The National Communication Association’s “Credo for Ethical Communication” states that we should be accountable for the long- and short-term effects of our communication (National Communication Association, 2012). The way we talk, the words we choose to use, and the actions we take after we are done speaking are all important aspects of communication ethics. Knowing that language can have real effects for people increases our need to be aware of the ethical implications of what we say. Hate speech and bias are important aspects of communication ethics on language and culture. In this section, we will focus on civility and accountability.
Civility
Our strong emotions regarding our own beliefs, attitudes, and values can sometimes lead to incivility in our verbal communication. Incivility occurs when a person deviates from established social norms. It can take many forms, including insults, bragging, bullying, gossiping, swearing, deception, and defensiveness, among others (Miller, 2001). Some people lament that we live in a time when civility is diminishing, but since standards and expectations for what is considered civil communication have changed over time, this isn’t the only time such claims have been made (Miller, 2001). As individualism and affluence have increased in many societies, so have the number of idiosyncratic identities that people feel they have the right to express. These increases could contribute to the impression that society is becoming less civil, when in fact it is just becoming different. As we learned in our section on perception and personality, we tend to assume other people are like us, and we may be disappointed or offended when we realize they are not. Cultural changes have probably contributed to making people less willing to engage in self-restraint, which again would be seen as uncivil by people who prefer a more restrained and self-controlled expression (Miller, 2001). The following are some common individual and situational influences that may lead to breaches of civility (Miller, 2001):
- Individual differences. Some people differ in their interpretations of civility in various settings, and some people have personality traits that may lead to actions deemed uncivil on a more regular basis.
- Ignorance. In some cases, especially in novel situations involving uncertainty, people may not know what social norms and expectations are.
- Lack of skill. Even when we know how to behave, we may not be able to do it. Such frustrations may lead a person to revert to undesirable behavior such as engaging in personal attacks during a conflict because they do not know what else to do.
- Lapse of control. Self-control is not an unlimited resource. Even when people know how to behave and have the skill to respond to a situation appropriately, they may not do so. Even people who are careful to monitor their behavior have occasional slipups.
- Negative intent. Some people, in an attempt to break with conformity or challenge societal norms, or for self-benefit (publicly embarrassing someone in order to look cool or edgy), are openly uncivil. Such behavior can also result from mental or psychological stresses or illnesses.
Polarizing Language
Philosophers of language have long noted our tendency to represent the world in very narrow ways when we feel threatened (Hayakawa & Hayakawa, 1990). This misrepresents reality and closes off dialogue. Although in our everyday talk we describe things in nuanced and measured ways, quarrels and controversies often narrow our vision, which is reflected in our vocabulary. In order to maintain a civil discourse in which people interact ethically and competently, it has been suggested that we keep an open mind and an open vocabulary.
One feature of communicative incivility is polarizing language, which refers to language that presents people, ideas, or situations as polar opposites. Such language exaggerates differences and overgeneralizes. Things are not simply black or white, right or wrong, or good or bad. Being able to see only two values and clearly accepting one and rejecting another does not indicate sophisticated or critical thinking. We do not have to accept every viewpoint as right and valid, and we can still hold strongly to our own beliefs and defend them without ignoring other possibilities, rejecting, or alienating others. A citizen who says, “All cops are corrupt,” is just as wrong as the cop who says, “All drug users are scum.” In avoiding polarizing language, we keep a more open mind, which may lead us to learn something new. A citizen may have a personal story about a negative encounter with a police officer that could enlighten us on his or her perspective, but the statement also falsely overgeneralizes that experience. Avoiding polarizing language can help us avoid polarized thinking, and the new information we learn may allow us to better understand and advocate for our position. Avoiding sweeping generalizations allows us to speak more clearly and avoid defensive reactions from others that result from such blanket statements.
Swearing
Scholars have identified two main types of swearing: social swearing and annoyance swearing (Baruch & Jenkins, 2007). People engage in social swearing to create social bonds or for impression management (to seem cool or attractive). This type of swearing is typically viewed as male dominated, but some research studies have shown that the differences in frequency and use of swearing by men and women are not as vast as perceived. Nevertheless, there is generally more of a social taboo against women swearing than men, but as you already know, communication is contextual. Annoyance swearing provides a sense of relief, as people use it to manage stress and tension, which can be a preferred alternative to physical aggression. In some cases, swearing can be cathartic, allowing a person to release emotions that might otherwise lead to more aggressive or violent actions.
Accountability
The complexity of our verbal language system allows us to present inferences as facts and mask judgments within seemingly objective or oblique language. As an ethical speaker and a critical listener, it is important to be able to distinguish between facts, inferences, and judgments (Hayakawa & Hayakawa, 1990). Inferences are conclusions based on thoughts or speculation, but not direct observation. Facts are conclusions based on direct observation or group consensus. Judgments are expressions of approval or disapproval that are subjective and not verifiable.
Linguists have noted that a frequent source of miscommunication is inference-observation confusion, or the misperception of an inference (conclusion based on limited information) as an observation (an observed or agreed-on fact) (Haney, 1992). We can see the possibility for such confusion in the following example: If a student posts on a professor-rating site the statement “This professor grades unfairly and plays favorites,” then they are presenting an inference and a judgment that could easily be interpreted as a fact. Using some of the strategies discussed earlier for speaking clearly can help present information in a more ethical way—for example, by using concrete and descriptive language and owning emotions and thoughts through the use of “I language.” To help clarify the message and be more accountable, the student could say, “I worked for three days straight on my final paper and only got a C,” which we will assume is a statement of fact. This could then be followed up with “But my friend told me she only worked on hers the day before it was due and she got an A. I think that’s unfair and I feel like my efforts aren’t recognized by the professor.” Of the last two statements, the first states what may be a fact (note, however, that the information is secondhand rather than directly observed) and the second states an inferred conclusion and expresses an owned thought and feeling. Sometimes people do not want to mark their statements as inferences because they want to believe them as facts. In this case, the student may have attributed her grade to the professor’s “unfairness” to cover up or avoid thoughts that her friend may be a better student in this subject area, a better writer, or a better student in general. Distinguishing between facts, inferences, and judgments, however, allows your listeners to better understand your message and judge the merits of it, which makes us more accountable and therefore more ethical speakers.
3.3 Language, Society, and Culture
Society and culture influence the words that we speak, and the words that we speak influence society and culture. Such a cyclical relationship can be difficult to understand, but many of the examples here and examples from our own lives help illustrate this point. One of the best ways to learn about society, culture, and language is to seek out opportunities to go beyond our typical comfort zones. Studying abroad, for example, brings many challenges that can turn into valuable lessons.
Language and Social Context
We arrive at meaning through conversational interaction, which follows many social norms and rules. As we have already learned, rules are explicitly stated conventions (“Look at me when I’m talking to you.”) and norms are implicit (saying you have to leave before you actually do to initiate politely the end to a conversation). To help conversations function meaningfully, we have learned social norms and internalized them to such an extent that we do not often consciously enact them. Instead, we rely on routines and roles (as determined by social forces) to help us proceed with verbal interaction, which also helps determine how a conversation will unfold. Our various social roles influence how we speak. For example, a person may say, “As a longtime member of this community…” or “As a first-generation college student…” Such statements cue others into the personal and social context from which we are speaking, which helps them better interpret our meaning.
One social norm that structures our communication is turn taking. People need to feel like they are contributing something to an interaction, so turn taking is a central part of how conversations play out (Crystal, 2005). Although we sometimes talk at the same time as others or interrupt them, there are numerous verbal and nonverbal cues, almost like a dance, that are exchanged between speakers that let people know when their turn will begin or end. Conversations do not always neatly progress from beginning to end with shared understanding along the way. There is a back and forth that is often verbally managed through rephrasing (“Let me try that again,”) and clarification (“Does that make sense?”) (Crystal, 2005)
Ending a conversation is similarly complex. Just walking away or ending a conversation without engaging in socially acceptable “leave-taking behaviors” would be considered a breach of social norms. Topic changes are often places where people can leave a conversation, but it is still routine for us to give a special reason for leaving, often in an apologetic tone (whether we mean it or not). Generally, though, conversations end through the cooperation of both people, as they offer and recognize typical signals that a topic area has been satisfactorily covered or that one or both people need to leave. It is customary in the United States for people to say they have to leave before they actually do and for that statement to be dismissed or ignored by the other person until additional leave-taking behaviors are enacted. When such cooperation is lacking, an awkward silence or abrupt ending can result, and as we have already learned, US Americans are not big fans of silence. Silence is not viewed the same way in other cultures, which leads us to our discussion of cultural context.
Language and Cultural Context
Culture is not solely determined by a person’s native language or nationality. It’s true that languages vary by country and region and that the language we speak influences our realities, but even people who speak the same language experience cultural differences because of their various intersecting cultural identities and personal experiences. We have a tendency to view our language as a whole more favorably than other languages. Although people may make persuasive arguments regarding which languages are more pleasing to the ear or difficult or easy to learn than others, no one language enables speakers to communicate more effectively than another (McCornack, 2007).
From birth, we are socialized into our various cultural identities. As with the social context, this acculturation process is a combination of explicit and implicit lessons. A child in Colombia, which is considered a more collectivist country in which people value group membership and cohesion over individualism, may not be explicitly told, “You are a member of a collectivistic culture, so you should care more about the family and community than yourself.” This cultural value would be transmitted through daily actions and through language use. Just as babies acquire knowledge of language practices at an astonishing rate in their first two years of life, so do they acquire cultural knowledge and values that are embedded in those language practices. At nine months old, it is possible to distinguish babies based on their language. Even at this early stage of development, when most babies are babbling and just learning to recognize but not wholly reproduce verbal interaction patterns, a Colombian baby would sound different from a Brazilian baby, even though neither would actually be using words from their native languages of Spanish and Portuguese (Crystal, 2005).
Customs and Norms
Social norms are culturally relative. The words used in politeness rituals in one culture can mean something completely different in another. For example, thank you in American English acknowledges receiving something (a gift, a favor, a compliment), in British English it can mean “yes” similar to American English’s yes, please, and in French merci can mean “no” as in “no, thank you” (Crystal, 2005). Additionally, what is considered a powerful language style varies from culture to culture. Confrontational language, such as swearing, can be seen as powerful in Western cultures, even though it violates some language taboos, but would be seen as immature and weak in Japan (Wetzel, 1988).
Gender also affects how we use language, but not to the extent that most people think. Although there is a widespread belief that men are more likely to communicate in a clear and straightforward way and women are more likely to communicate in an emotional and indirect way, a meta-analysis of research findings from more than two hundred studies found only small differences in the personal disclosures of men and women (Dindia & Allen, 1992). Men and women’s levels of disclosure are even more similar when engaging in cross-gender communication, meaning men and woman are more similar when speaking to each other than when men speak to men or women speak to women. This could be due to the internalized pressure to speak about the other gender in socially sanctioned ways, in essence reinforcing the stereotypes when speaking to the same gender but challenging them in cross-gender encounters. Researchers also dispelled the belief that men interrupt more than women do, finding that men and women interrupt each other with similar frequency in cross-gender encounters (Dindia, 1987). These findings, which state that men and women communicate more similarly during cross-gender encounters and then communicate in more stereotypical ways in same-gender encounters, can be explained with communication accommodation theory.
Language and Cultural Bias
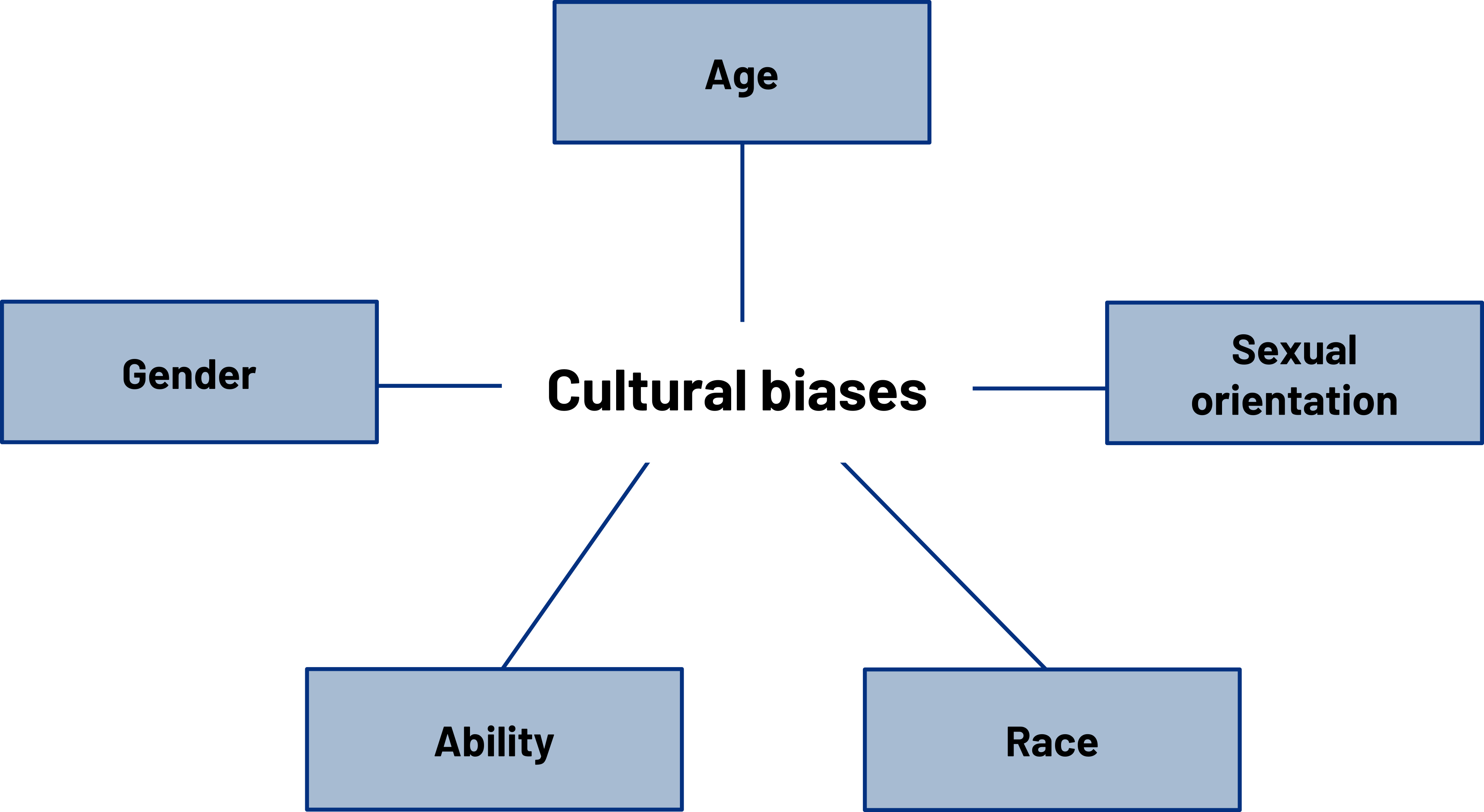
Cultural bias is a skewed way of viewing or talking about a group negatively. Bias has a way of creeping into our daily language use, often under our awareness. Culturally biased language can refer to one or more cultural identities, including race, gender, age, sexual orientation, and ability. Much biased language is based on stereotypes and myths that influence the words we use. Bias is both intentional and unintentional, but as we’ve already discussed, we have to be accountable for what we say even if we didn’t “intend” a particular meaning—remember, meaning is generated; it doesn’t exist inside our thoughts or words. We will discuss specific ways in which cultural bias manifests in our language and ways to become more aware of bias. Becoming aware of and addressing cultural bias is not the same thing as engaging in “political correctness.” Political correctness takes awareness to the extreme but does not do much to address cultural bias aside from make people feel like they are walking on eggshells. That kind of pressure can lead people to avoid discussions about cultural identities or avoid people with different cultural identities. Our goal is not to eliminate all cultural bias from verbal communication or to never offend anyone, intentionally or otherwise. Instead, we will continue to use guidelines for ethical communication that we have already discussed and strive to increase our competence.
Race
People sometimes use euphemisms for race that illustrate bias because the terms are implicitly compared to the dominant group (Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, 2019). For example, referring to a person as “urban” or a neighborhood as “inner city” can be an accurate descriptor, but when such words are used as a substitute for racial identity, they illustrate cultural biases that equate certain races with cities and poverty. Using adjectives like articulate or well dressed in statements like “My black coworker is articulate” reinforces negative stereotypes even though these words are typically viewed as positive. Terms like nonwhite set up whiteness as the norm, which implies that white people are the norm against which all other races should be compared. Biased language also reduces the diversity within certain racial groups—for example, referring to anyone who looks like they are of Asian descent as Chinese or everyone who “looks” Latino/a as Mexicans. Some people with racial identities other than white, including people who are multiracial, use the label person/people of color to indicate solidarity among groups, but it is likely that they still prefer a more specific label when referring to an individual or referencing a specific racial group.
Gender
Language has a tendency to exaggerate perceived and stereotypical differences between men and women. The use of the term opposite sex presumes that men and women are opposites, like positive and negative poles of a magnet, which is obviously not true, or men and women would not be able to have successful interactions or relationships. A term like other gender does not presume opposites and acknowledges that male and female identities and communication are more influenced by gender, which is the social and cultural meanings and norms associated with males and females, than sex, which is the physiology and genetic makeup of a male and female.
One key to avoiding gendered bias in language is to avoid the generic use of he when referring to something relevant to males and females. Instead, you can informally use a gender-neutral pronoun like they or their or you can use his or her (Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, 2019). When giving a series of examples, you can alternate usage of masculine and feminine pronouns, switching with each example. We have lasting gendered associations with certain occupations that have tended to be male or female dominated, which erase the presence of both genders. Other words reflect the general masculine bias present in English. The following word pairs show the gender-biased term followed by an unbiased term: waitress/server, chairman/chair or chairperson, mankind/people, cameraman/camera operator, mailman/postal worker, sportsmanship/fair play. Common language practices also tend to infantilize women but not men, when, for example, women are referred to as chicks, girls, or babes. Since there is no linguistic equivalent that indicates the marital status of men before their name. Using Ms. instead of Miss or Mrs. helps reduce bias.
Age
Language that includes age bias can be directed toward older or younger people. Descriptions of younger people often presume recklessness or inexperience, while those of older people presume frailty or disconnection. The term elderly generally refers to people over sixty-five, but it has connotations of weakness, which is not accurate because there are plenty of people over sixty-five who are stronger and more athletic than people in their twenties and thirties. Even though it is generic, older people does not really have negative implications. More specific words that describe groups of older people include grandmothers/grandfathers (even though they can be fairly young too), retirees, or people over sixty-five (Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, 2019). Referring to people over the age of eighteen as boys or girls is not typically viewed as appropriate.
Sexual Orientation
Discussions of sexual and affectional orientation range from everyday conversations to contentious political and personal debates. The negative stereotypes that have been associated with homosexuality, including deviance, mental illness, and criminal behavior, continue to influence our language use (American Psychological Association, 2019). Terminology related to gay, lesbian, and bisexual (GLB) people can be confusing, so let’s spend some time raise our awareness about preferred labels. First, sexual orientation is the term preferred to sexual preference. Preference suggests a voluntary choice, as in someone has a preference for cheddar or American cheese, which doesn’t reflect the experience of most GLB people or research findings that show sexuality is more complex. You may also see affectional orientation included with sexual orientation because it acknowledges that GLB relationships, like heterosexual relationships, are about intimacy and closeness (affection) that is not just sexually based. Most people also prefer the labels gay, lesbian, or bisexual to homosexual, which is clinical and does not so much refer to an identity as a sex act.
Ability
People with disabilities make up a diverse group that has increasingly come to be viewed as a cultural/social identity group. People without disabilities are often referred to as able-bodied. As with sexual orientation, comparing people with disabilities to “normal” people implies that there is an agreed-on definition of what “normal” is and that people with disabilities are “abnormal.” Disability is also preferred to the word handicap. Just because someone is disabled does not mean he or she is also handicapped. The environment around them rather than their disability often handicaps people with disabilities (Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, 2019). Ignoring the environment as the source of a handicap and placing it on the person fits into a pattern of reducing people with disabilities to their disability—for example, calling someone a paraplegic instead of a person with paraplegia. In many cases, as with sexual orientation, race, age, and gender, verbally marking a person as disabled is not relevant and does not need spotlighting. Language used in conjunction with disabilities also tends to portray people as victims of their disability and paint pictures of their lives as gloomy, dreadful, or painful. Such descriptors are often generalizations or completely inaccurate.
References
Figures
Figure 3.1: Triangle of meaning. Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0.
Table 3.1: Four types of verbal expressions. Adapted from Matthew McKay, Martha Davis, and Patrick Fanning, Messages: Communication Skills Book, 2nd ed. (Oakland, CA: New Harbinger Publications, 1995), 34–36.
Figure 3.2: “Google” is a neologism; the term went from being just a noun to both a noun and a verb. Nathana Rebouças. 2020. Unsplash license. https://unsplash.com/photos/O5v8heKY4cI
Figure 3.3: Example of a supportive message. Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0.
Figure 3.4: Example of an unsupportive message. Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0.
Figure 3.5: Ladder of abstraction. Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0. Adapted under fair use from S. I. Hayakawa and Alan R. Hayakawa, Language in Thought and Action, 5th ed. (San Diego, CA: Harcourt Brace, 1990), 85.
Figure 3.6: Common types of cultural bias. Kindred Grey. 2022. CC BY 4.0.
Section 3.1
Abram, D. (1997). Spell of the sensuous: Perception and language in a more-than-human world. Vintage Books.
Barthes, R. (1972). Mythologies (A. Lavers, Trans.). Hill and Wang.
Brown, G. A. (2006). Explaining. In O. Hargie (Ed.),The handbook of communication skills. Routledge.
Crystal, D. (2005). How language works: How babies babble, words change meaning, and languages live or die. Overlook Press.
Hargie, O. (2011). Skilled interpersonal interaction: Research, theory, and practice. Routledge.
Hayakawa, S. I., & Hayakawa, A. R. (1990). Language in thought and action (5th ed.). Harcourt Brace.
Holocaust and Human Rights Education Center. (n.d.). Lesson 4: 1939–1942, Persecution and segregation. Retrieved November 11, 2021 from https://hhrecny.app.neoncrm.com/np/clients/hhrecny/product.jsp?product=26&
McCornack, S. (2007). Reflect and relate: An introduction to interpersonal communication. Bedford/St Martin’s.
McKay, M., Davis, M., & Fanning, P. (1995). Messages: Communication skills book (2nd ed.). New Harbinger Publications.
Ogden, C.K., & Richards, I.A. (1923). The meaning of meaning. Harcourt, Brace.
Section 3.2
Allan, K., & Burridge, K. (2006). Forbidden words: Taboo and the censoring of language. Cambridge University Press.
Baruch, Y., & Jenkins, S. (2007). Swearing at work and permissive leadership culture: When anti-social becomes social and incivility is acceptable. Leadership & Organization Development Journal, 28(6), 492–507. https://doi.org/10.1108/01437730710780958
Hayakawa, S. I., & Hayakawa, A. R. (1990). Language in thought and action (5th ed.). Harcourt Brace.
Haney, W. V. (1992). Communication and Interpersonal relations: Text and cases. Pennsylvania State University Press.
Miller, R. S. (2001). Breaches of propriety. In R. M. Kowalski (Ed.), Behaving badly: Aversive behaviors in interpersonal relationships (pp. 29–58). American Psychological Association. https://doi.org/10.1037/10365-002
National Communication Association. (2017). NCA credo for ethical communication. Retrieved November 12, 2021 from https://www.natcom.org/sites/default/files/Public_Statement_Credo_for_Ethical_Communication_2017.pdf
Olbricht, T. H. (1968). Informative speaking. Scott, Foresman.
Yaguello, M. (1998). Language through the looking glass: Exploring language and linguistics. Oxford University Press.
Section 3.3
American Psychological Association. (2019). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association 7th ed.). American Psychological Association.
American Psychological Association. (2019). Supplemental resources. https://apastyle.apa.org/products/supplemental-resources
Crystal, D. (2005). How language works: How babies babble, words change meaning, and languages live or die. Overlook Press.
Dindia, K. (1987). The effect of sex of subject and sex of partner on interruptions. Human Communication Research, 13(3), 345-371. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2958.1987.tb00109.x
Dindia, K., & Allen, M. (1992). Sex differences in self-disclosure: A meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 112(1), 106–124. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.112.1.106
McCornack, S. (2007). Reflect and relate: An introduction to interpersonal communication. Bedford/St Martin’s.
Something that stands in for or represents something else
Culturally agreed on and ever-changing systems of symbols that help us organize, understand and generate meaning
Refers to our ability to talk and events that are removed in space or time from a speaker and situation
A model of communication that indicates the relationship among a thought, symbol, and referent and highlights indirect relationship between the symbol and referent
Refers to definitions that are accepted by the language group as a whole, or the dictionary definition of a word
Refers to the definitions that are based on emotion- or experience-based associations people have with a word
Refers to the rules that govern how words are used to make phrases and sentences
Language is expressive. Helps us communicate our observations, thoughts, feelings, and needs
Refers to new or adapted words that are specific to one group, context, or time period
Refers to specialized words used by certain group or profession
A direct comparison of two things using the words like or as
An implicit comparison of two things that are not alike and/or are not typically associated
Conclusions based on thoughts or speculation, but not direct observation
Conclusions based on direct observation or group consensus

